Can Kaspa Outpace Bitcoin? Comparing Two Proof-of-Work Titans

Compare Kaspa and Bitcoin's proof-of-work models, technical strengths, scalability, and adoption in this in-depth blockchain analysis.
Miracle Nwokwu
August 7, 2025
Table of Contents
The cryptocurrency landscape has been shaped by Bitcoin’s pioneering vision of decentralized, peer-to-peer money. Since its launch in 2009, Bitcoin has solidified its place as the gold standard of digital assets, often dubbed "digital gold" for its scarcity and store-of-value properties. Enter Kaspa, a newer Layer-1 blockchain launched in 2021, which claims to offer superior speed and scalability while adhering to Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) ethos. Both networks aim to deliver secure, decentralized transactions, but they diverge in design, goals, and execution.
This article examines the strengths and trade-offs of Kaspa and Bitcoin, comparing their technical architectures, adoption levels, and potential roles in the future of finance.
The Foundations: Bitcoin’s Legacy vs. Kaspa’s Ambition
Bitcoin, created by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, introduced the world to blockchain technology with its 2008 whitepaper. Launched in 2009, it operates on a linear blockchain, processing one block roughly every 10 minutes. This deliberate pace prioritizes security and decentralization, ensuring that nodes worldwide can synchronize without centralized control. Bitcoin’s fixed supply of 21 million coins, with the last to be mined around 2140, reinforces its scarcity-driven value proposition. Its halving events, occurring approximately every four years, gradually reduce miner rewards, mimicking the extraction of finite resources like gold.
Kaspa, founded by Dr. Yonatan Sompolinsky and inspired by Nakamoto’s principles, takes a different approach. Launched on November 7, 2021, with no premine or pre-sales, Kaspa emphasizes fairness and community-driven development. Unlike Bitcoin’s linear chain, Kaspa employs a blockDAG (Directed Acyclic Graph) structure, allowing multiple blocks to be processed simultaneously.
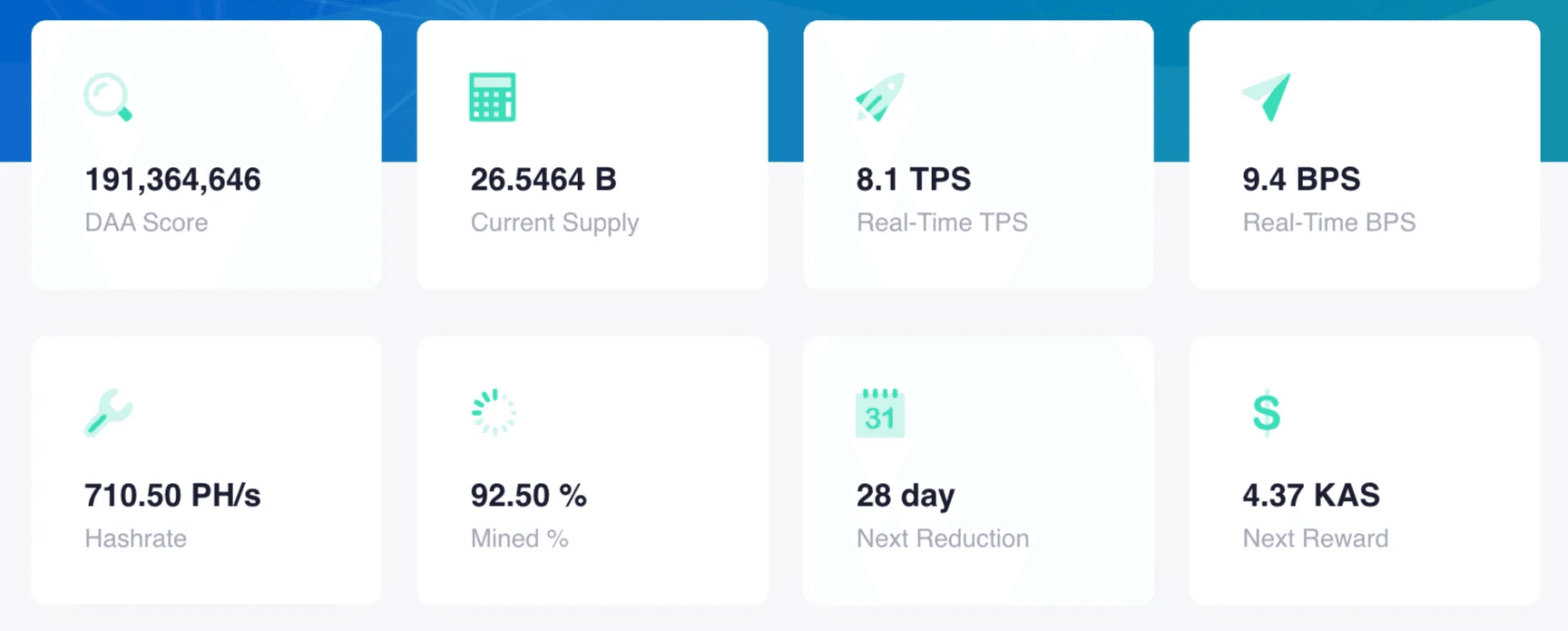
This design, powered by the GHOSTDAG protocol, enables Kaspa to achieve up to 10 blocks per second and process 3,000–4,000 transactions per second (TPS) with 10-second confirmation times, as reported in March 2025 network metrics. Kaspa’s maximum supply is capped at 28.7 billion coins, with a smoother “chromatic” emission schedule that reduces rewards monthly by a factor of (1/2)^(1/12), halving annually.
Speed and Scalability: Kaspa’s Edge
Kaspa’s blockDAG architecture is its defining feature. Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin discard “orphan” blocks—valid blocks created simultaneously but not included in the main chain—leading to inefficiencies. Kaspa’s GHOSTDAG protocol integrates these blocks into a directed acyclic graph, classifying them as “blue” (honest, well-connected) or “red” (potentially malicious). This allows parallel block creation, dramatically increasing throughput without sacrificing security. Following the Crescendo Hardfork in May 2025, Kaspa’s mainnet scaled from 1 to 10 blocks per second, with plans to reach 100 blocks per second in the future. This speed enables near-instant transaction confirmations, making Kaspa suitable for high-frequency use cases like microtransactions or retail payments.
Bitcoin, by contrast, prioritizes stability over speed. Its 10-minute block time ensures robust network synchronization, even in low-bandwidth environments, but limits transaction throughput to about 7 TPS. This bottleneck has led to higher fees during network congestion—sometimes exceeding $4 per transaction, compared to Kaspa’s sub-cent fees. Bitcoin’s scalability challenges are partly addressed by Layer-2 solutions like the Lightning Network, which enables faster, cheaper off-chain transactions. However, these solutions introduce complexity and require trust in secondary layers, unlike Kaspa’s native Layer-1 scalability.
Security and Decentralization: Bitcoin’s Fortress
Bitcoin’s security model is battle-tested. Its PoW consensus, secured by the SHA-256 algorithm, requires miners to solve computationally intensive puzzles, making 51% attacks prohibitively expensive. With a global network of thousands of nodes and a hashrate distributed across major mining pools, Bitcoin’s decentralization is unmatched. Its longevity—over 15 years without a major security breach—has cemented its reputation as the most secure blockchain. The fixed 10-minute block interval minimizes the risk of chain reorganizations, ensuring transaction finality.
Kaspa also uses PoW, employing the kHeavyHash algorithm, which is designed to be energy-efficient and compatible with both GPUs and ASICs. The GHOSTDAG protocol maintains Bitcoin-like security by favoring well-connected blocks, protecting against double-spending attacks. However, Kaspa’s rapid block rate introduces challenges. Sub-second block intervals demand tighter network synchronization, which could strain nodes with limited bandwidth or processing power. While Kaspa’s hashrate has grown significantly since the introduction of ASIC miners like Bitmain’s Antminer KS5 in 2024, its network is younger and less tested under adversarial conditions. Bitcoin’s established infrastructure and miner distribution give it a clear edge in decentralization and resilience.
Tokenomics and Distribution: Fairness and Scarcity
Both Bitcoin and Kaspa emphasize fair launches, with no premines or insider allocations. Bitcoin’s 21 million coin cap is iconic, with approximately 19.7 million coins in circulation as of August 2025. Its halving events create sharp supply reductions, which historically correlate with price increases, though they can disrupt miner incentives. Kaspa’s 28.7 billion coin cap, with 26.54 billion circulating as of writing, follows a smoother emission curve. The chromatic schedule reduces rewards gradually, potentially stabilizing miner income and market supply. Analysis from March 2025 shows Kaspa’s token distribution is relatively balanced, with 70% of addresses holding 0.01–10,000 KAS and only 17 addresses holding over 100 million KAS, suggesting less concentration than some competing projects.
Bitcoin’s scarcity narrative drives its “digital gold” status, appealing to institutional investors and hodlers. Kaspa, named after the Aramaic word for “silver,” positions itself as a medium of exchange for daily transactions. While Bitcoin’s limited supply fuels long-term value storage, Kaspa’s higher supply and faster issuance may better suit high-velocity economies, though it dilutes its scarcity appeal.
Adoption and Ecosystem: Bitcoin’s Dominance
Bitcoin’s first-mover advantage is undeniable. It boasts a market capitalization exceeding $2 trillion, with widespread acceptance by merchants, institutions, and even nation-states like El Salvador, which adopted it as legal tender in 2021. The approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the U.S. in 2024 further legitimized it as an investment asset. Bitcoin’s ecosystem includes robust infrastructure—wallets, exchanges, and payment processors—making it accessible to millions. However, its slow transaction speeds and high fees limit its use for everyday purchases, pushing reliance on Layer-2 solutions.
Kaspa, while newer, has built a dedicated community across 16+ countries, with open-source contributions on GitHub. Its integration into exchanges like Gate.io and MEXC, and support for hardware wallets like Ledger, signals growing adoption. The Crescendo Hardfork introduced features like payload support and additive addresses, laying the groundwork for smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Kaspa’s Layer-2 plans, including ZK-rollups, aim to expand its ecosystem further. Yet, its market cap, around $2.3 billion as of writing, and limited mainstream recognition pale in comparison to Bitcoin’s global footprint.
Energy Efficiency and Mining Accessibility
Bitcoin’s PoW mining, while secure, is energy-intensive, drawing criticism for its environmental impact. Large-scale mining operations, often using specialized ASICs, dominate the network, making it less accessible to individual miners. Kaspa’s kHeavyHash algorithm, designed for energy efficiency, allows mining with GPUs and ASICs, lowering the barrier to entry. Its blockDAG structure supports solo mining at lower hashrates, promoting decentralization. For example, Marathon Digital Holdings mined $16 million worth of KAS in 2024, diversifying from Bitcoin while maintaining high profit margins. Kaspa’s energy-efficient design aligns with growing demands for sustainable blockchain solutions, though its smaller scale means it faces less scrutiny than Bitcoin.
Future Prospects: Diverging Paths
Bitcoin’s roadmap focuses on maintaining its core strengths—security, decentralization, and scarcity—while improving scalability through Layer-2 solutions. The Lightning Network, for instance, aims to enable instant, low-cost transactions, though adoption remains uneven. Bitcoin’s entrenched position ensures it will remain a store of value, but its conservative design limits innovation in areas like smart contracts.
Kaspa’s ambitions are broader. The Rust rewrite, completed in 2024, and Testnet 11’s success at 2,400–3,000 TPS signal its potential to rival traditional payment systems. Upcoming features like smart contract support and KRC-20 token standards could position Kaspa as a platform for DeFi and dApps, areas where Bitcoin lags. However, Kaspa’s rapid evolution introduces risks, such as untested performance under high-load conditions or potential centralization as ASICs dominate mining.
A Balanced Perspective
Kaspa and Bitcoin represent distinct approaches to the PoW model. Kaspa excels in speed and scalability, offering a vision of blockchain as a high-throughput, low-cost transaction layer. Its blockDAG and GHOSTDAG innovations address limitations that Bitcoin’s linear chain cannot, making it a compelling choice for applications requiring fast confirmations. Bitcoin, however, remains the gold standard for security, decentralization, and adoption. Its global recognition and robust infrastructure make it the preferred choice for wealth preservation and institutional investment.
The comparison need not crown a winner. Kaspa’s speed and Bitcoin’s stability serve different needs within the cryptocurrency ecosystem. For users seeking rapid, low-cost transactions, Kaspa’s design is a leap forward. For those prioritizing battle-tested security and widespread acceptance, Bitcoin is unrivaled. As both networks evolve, their interplay may shape the future of decentralized finance, with Kaspa pushing the boundaries of what PoW can achieve and Bitcoin anchoring the industry with its enduring reliability.
Sources:
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes Kaspa faster than Bitcoin?
Kaspa's speed advantage comes from its blockDAG architecture, which allows multiple blocks to be created and confirmed in parallel. Unlike Bitcoin’s linear chain that processes one block every 10 minutes, Kaspa achieves up to 10 blocks per second with 3,000–4,000 transactions per second, enabling near-instant confirmations.
How does Kaspa’s GHOSTDAG protocol work?
Kaspa’s GHOSTDAG protocol organizes blocks into a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) rather than a single chain. It classifies blocks as "blue" (honest) or "red" (less connected) to integrate parallel block creation securely, reducing orphaned blocks and improving scalability without sacrificing decentralization.
How do Kaspa and Bitcoin differ in supply and tokenomics?
Bitcoin has a fixed supply of 21 million coins with halving events every four years. Kaspa’s maximum supply is 28.7 billion, and it uses a smoother chromatic emission curve that halves rewards annually but reduces them monthly. This allows for more stable miner rewards and potentially smoother token distribution.
Is Kaspa more energy efficient than Bitcoin?
Yes, Kaspa is designed to be more energy efficient. It uses the kHeavyHash algorithm, which supports both GPU and ASIC mining, lowering the barrier to entry and allowing for solo mining. This contrasts with Bitcoin’s energy-intensive SHA-256 mining dominated by industrial ASIC farms.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Miracle Nwokwu
Miracle NwokwuMiracle holds undergraduate degrees in French and Marketing Analytics and has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology since 2016. He specializes in technical analysis and on-chain analytics, and has taught formal technical analysis courses. His written work has been featured across multiple crypto publications including The Capital, CryptoTVPlus, and Bitville, in addition to BSCN.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens