What is Bitcoin and How Does it Work?

Learn what Bitcoin is, how blockchain technology works, mining processes, and why it's called digital gold in this complete guide.
Crypto Rich
January 29, 2025
Table of Contents
Last Revision: August 8, 2025
Bitcoin is the world's first and most valuable cryptocurrency, operating as a decentralized digital currency that is not controlled by banks or governments. Created in 2009 by the pseudonymous Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin uses blockchain technology and proof-of-work mining to secure transactions and maintain a fixed supply of 21 million coins - earning it the nickname "digital gold." The cryptocurrency reached an all-time high exceeding $122,000 in mid-2025 amid growing institutional adoption and supportive policies. This milestone reflects Bitcoin's maturation as an asset class, with circulating supply approaching 20 million coins and market dominance enduring amid broader crypto growth.
As digital gold in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, Bitcoin's proof-of-work model and blockchain innovation set the standard for secure, borderless value transfer across the global financial landscape.
How Did Bitcoin Begin?
The story of Bitcoin begins during the 2008 financial crisis when trust in traditional banking reached historic lows. An anonymous person or group using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper titled "Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System." This document outlined a revolutionary vision for digital money that could operate without intermediaries like banks or governments.
Bitcoin’s layer one chain officially launched on January 3, 2009. Satoshi Nakamoto mined the genesis block and created the first 50 bitcoins. The timing proved significant - it occurred amid widespread financial turmoil when public trust in traditional institutions had collapsed. The block included an embedded message critiquing fiat bailouts: "Chancellor on brink of second bailout for banks" - highlighting Bitcoin's philosophical roots in financial independence.

The First Bitcoin Transaction
The first real-world Bitcoin transaction occurred in May 2010. Programmer Laszlo Hanyecz paid 10,000 BTC for two pizzas. Now commemorated as "Bitcoin Pizza Day," this transaction would be worth over $1.2 billion at today's prices - perfectly illustrating Bitcoin's dramatic appreciation over 15 years.
How Does Bitcoin Actually Work?
Understanding Bitcoin requires grasping the revolutionary technology that powers it. The system operates on blockchain technology - a distributed ledger recording all transactions across thousands of computers worldwide. This decentralized approach eliminates single points of failure while ensuring no central authority can manipulate the system.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
The blockchain represents more than just a digital ledger. It's an innovative approach to data integrity that forms the foundation of Bitcoin's revolutionary design.
Cryptographic Hashing and Chain Structure
Bitcoin's blockchain uses cryptographic hashing, where each block's data gets condensed into a unique "fingerprint" via algorithms like SHA-256. Change even one character in a transaction? The hash output changes completely, making tampering instantly detectable.
This creates an unbreakable chain. Each new block references the previous one's hash. Want to alter history? You'd need to recalculate all subsequent blocks across thousands of nodes - a computationally impossible task.
Block Architecture and Data Organization
Bitcoin's blockchain structure consists of interconnected components working together seamlessly. Each block contains a header with metadata and a body containing transactions. The block header includes several key elements: the version number, a reference to the previous block's hash, a Merkle root summarizing all transactions, timestamp, difficulty target, and a nonce that miners manipulate to solve the proof-of-work puzzle.
Merkle trees provide efficient transaction verification without downloading entire blocks. These binary tree structures hash pairs of transactions repeatedly until reaching a single root hash. This clever design allows light clients to verify specific transactions by downloading only the relevant branch of the tree, rather than every transaction in a block.
Address Formats and User Interface
Bitcoin addresses represent hashed public keys rather than the keys themselves, adding privacy and security layers. Modern Bitcoin uses several address formats, including Legacy (starting with "1"), SegWit-compatible (starting with "3"), and native SegWit addresses (starting with "bc1"). Each format offers different features, with newer formats providing lower transaction fees and improved efficiency.
Key Components of Bitcoin's Infrastructure
Bitcoin's network architecture consists of several interconnected elements working together to maintain security and functionality. Over 10,000 nodes worldwide independently verify transactions - ensuring no single point of failure. This contrasts sharply with centralized systems like banks, where one hack or shutdown can halt operations entirely.
Users sign transactions with private keys (cryptographic proofs of ownership), then broadcast them to the network. Miners bundle these transactions into blocks every 10 minutes, with transaction fees (denominated in satoshis per virtual byte) allowing users to prioritize speed during congestion. Multiple confirmations ensure finality, with most services requiring six confirmations for high-value transactions. Once confirmed, transactions become practically irreversible. The network's collective computational power makes rewriting transaction history economically unfeasible.
Transaction Lifecycle
Understanding how a Bitcoin transaction moves from initiation to final confirmation reveals the elegant mechanics underlying the network. A typical transaction begins when wallet software creates and signs a transfer using private keys, mathematically proving ownership without revealing the keys themselves. The signed transaction broadcasts to nodes across the network for validation against consensus rules, like preventing double-spending and ensuring sufficient balances.
Unconfirmed transactions enter the mempool (memory pool) where miners select them based on fee rates and transaction size. Higher fees incentivize faster inclusion, while lower fees may wait during busy periods. Once a miner includes the transaction in a solved block, it receives its first confirmation. Additional blocks built on top provide more confirmations, with six confirmations considered highly secure for large transfers. This process combines speed with security, enabling users to select their preferred balance through fee customization.
What is Bitcoin Mining and How Does Proof-of-Work Secure the Network?
Bitcoin mining represents one of the most misunderstood aspects of cryptocurrency technology. Contrary to popular belief, Bitcoin mining isn't random puzzle-solving. It's tied to real-world physics and economics. Miners expend energy to solve SHA-256 puzzles, converting electricity into heat via thermodynamic laws while organizing data into secure blocks using a consensus mechanism called Proof of Work (PoW).
The Mining Process Explained
Understanding how Bitcoin mining works requires examining both technical and economic mechanisms. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems using specialized hardware called ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). The first miner to solve the puzzle gets to add the new block to the blockchain. Their reward? Newly created bitcoins.
Currently, miners receive 3.125 BTC per block following the 2024 halving event. This reward decreases by half approximately every four years, controlling Bitcoin's supply inflation and ensuring scarcity increases over time. The 2024 halving reduced rewards from the previous 6.25 BTC, reinforcing Bitcoin's programmed scarcity similar to previous halvings in 2012, 2016, and 2020.
Mining Hardware Evolution
Bitcoin mining has undergone dramatic technological evolution since its inception. In 2009, Satoshi Nakamoto and early adopters mined Bitcoin using regular computer CPUs. Any desktop computer could participate - making the network truly decentralized in its early days.
As Bitcoin's value increased, miners discovered that graphics cards (GPUs) could mine much more efficiently than CPUs. GPUs, designed for parallel processing in video games, proved excellent at the repetitive calculations required for Bitcoin mining. This GPU era lasted from roughly 2010 to 2013.
Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) briefly dominated mining around 2012-2013. These specialized chips offered better efficiency than GPUs while remaining programmable for different algorithms. However, their reign was short-lived.
The introduction of Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) transformed Bitcoin mining permanently. Unlike general-purpose processors, ASICs are designed exclusively for Bitcoin's SHA-256 algorithm. Modern ASIC miners like the Antminer S19 Pro can perform trillions of calculations per second while consuming far less electricity per hash than any previous technology.
This evolution means home mining is no longer profitable for most individuals. Industrial mining operations with cheap electricity, efficient cooling, and bulk hardware purchases now dominate the network. While this has centralized mining geographically, the protocol itself remains decentralized across thousands of independent operators worldwide.

Mining Economics and Pool Dynamics
Bitcoin mining is a competitive business where profitability depends on several key factors. Electricity costs typically represent 60-80% of mining expenses, making access to cheap power the primary determinant of success. Industrial miners seek locations with electricity prices below $0.05 per kilowatt-hour to maintain profitability.
Hardware costs create significant upfront investments. A single high-end ASIC miner costs $3,000-$10,000 and becomes obsolete within 2-3 years as more efficient models emerge. This rapid depreciation forces miners to generate returns quickly while planning for regular equipment upgrades.
Mining difficulty adjustments every 2,016 blocks (approximately two weeks) ensure blocks continue appearing every 10 minutes regardless of total network computing power. When more miners join, difficulty increases, making mining harder. When miners leave, difficulty decreases. This self-regulating mechanism maintains Bitcoin's predictable issuance schedule.
Most individual miners join mining pools to smooth out income volatility, as solo mining presents significant challenges:
- Income predictability - Pools distribute rewards proportionally, providing steady payouts instead of feast-or-famine solo mining
- Lower variance - Solo miners might wait months for rewards, then suddenly receive large payouts
- Reduced barriers - Smaller miners can participate meaningfully without industrial-scale operations
- Professional management - Pool operators handle technical complexities like node maintenance and payout distribution
- Backup infrastructure - Pools provide redundant systems, ensuring minimal downtime during hardware failures
Why Proof-of-Work Matters for Security
The proof-of-work consensus mechanism forms the backbone of Bitcoin's security model. Here's how it works: proof-of-work creates security through energy expenditure. Attacking the network would require controlling over 51% of the total computing power. Proof-of-work's energy requirements make 51% attacks prohibitively expensive, with costs estimated in the billions of dollars, ensuring long-term network integrity regardless of Bitcoin's market value.
This consensus mechanism provides multiple security benefits:
- Decentralized verification - No central authorities needed to validate transactions
- Economic security - Attacks require massive real-world resource investment
- Tamper resistance - Computational requirements make historical changes prohibitively expensive
- Network stability - Predictable block times maintain consistent operation
- Sybil resistance - Prevents fake node attacks by requiring provable work, unlike stake-based systems where influence scales with holdings
- Immutable records - Energy expenditure creates permanent, unchangeable transaction history
Mining Energy and Sustainability
Energy consumption remains one of Bitcoin's most debated aspects. Let's examine the facts. Bitcoin mining's energy use, comparable to that of a mid-sized country, increasingly draws from renewable and stranded sources like excess hydropower. Miners tap unused energy from remote locations where transmission losses make grid export inefficient. We're talking up to 50% loss over 500 miles.
But here's the interesting part: Bitcoin mining actually stabilizes electrical grids. How? By monetizing excess renewable output during peak production hours (such as solar during midday or hydropower in remote areas), mining turns potential waste into economic incentive for green infrastructure expansion. This flexible demand can shut off instantly during grid stress, providing valuable load balancing while converting stranded energy into secure digital value.
Industrial mining operations continue expanding while holding significant Bitcoin reserves, showcasing the industry's growth and institutional adoption trends.
Why is Bitcoin Called Digital Gold?
The comparison between Bitcoin and gold extends far beyond simple marketing rhetoric. Bitcoin earned the "digital gold" moniker through striking parallels with the precious metal. Both serve as stores of value, hedge against inflation, and maintain scarcity through resource-intensive production processes.

Scarcity and Fixed Supply
Bitcoin's supply mechanism represents a fundamental departure from traditional monetary systems. The protocol specifies that only 21 million coins will ever exist, with the last bitcoin expected to be mined around 2140. This built-in scarcity contrasts sharply with fiat currencies, which central banks can print at will. Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio - a scarcity metric - often surpasses gold's, quantifying its deflationary appeal to investors seeking hard assets.
Unlike gold, where new deposits might be discovered, Bitcoin's supply remains mathematically fixed and completely verifiable.
Superior Store of Value Properties
When examining Bitcoin's characteristics as a store of value, several key advantages over traditional gold become apparent:
- Durability - Digital records don't corrode, tarnish, or physically degrade over time, ensuring permanent preservation
- Portability - Bitcoin transfers globally in minutes, while gold requires physical transport or trusted intermediaries
- Divisibility - Each bitcoin divides into 100 million satoshis, enabling precise micro-transactions impossible with gold
- Verifiability - Blockchain technology provides cryptographic proof of authenticity, eliminating counterfeit concerns
- Storage costs - Digital wallets require no ongoing expenses, while gold demands secure vaults and insurance
Economic Parallels to Gold Mining
The relationship between Bitcoin creation and gold extraction reveals fascinating economic similarities. Both require significant energy investment, become more difficult over time, and produce assets with lasting value. Halvings every four years mimic gold's diminishing returns, driving scarcity-based price appreciation.
The key difference? Bitcoin's scarcity is absolutely guaranteed by mathematics, while gold's supply depends on geological discoveries and extraction technology.
What Are Bitcoin's Main Advantages?
Bitcoin offers several key benefits that distinguish it from traditional financial systems and other digital assets. These advantages stem from its unique technological architecture and philosophical approach to money.
Decentralization and Censorship Resistance
Bitcoin's decentralized structure provides unprecedented financial autonomy to users worldwide. No government, bank, or corporation controls Bitcoin. This decentralization provides financial sovereignty to users in authoritarian regimes where traditional banking systems can freeze accounts or confiscate assets.
Bitcoin enables financial sovereignty in regions with restrictive monetary policies, serving as a tool for the unbanked (estimated at billions globally) and those facing currency controls or inflation worldwide.
Transparency and Auditability
Bitcoin's public ledger creates unprecedented transparency in financial transactions. Every Bitcoin transaction is publicly recorded on the blockchain. Anyone can verify balances, transaction histories, and network statistics in real-time. This transparency eliminates the need to trust financial institutions or government assurances.
Global Accessibility
Bitcoin removes traditional barriers to financial participation that exclude billions of people worldwide. Bitcoin requires only internet access to participate. No bank accounts, credit checks, or government approvals needed. This opens financial services to billions of unbanked individuals worldwide who lack access to traditional banking infrastructure.
Programmable Money
Bitcoin's digital nature enables capabilities impossible with traditional physical currencies. Unlike simple value transfers, Bitcoin incorporates a scripting language called Bitcoin Script that allows for sophisticated transaction conditions and automated execution.
Multi-Signature and Time-Lock Features
Multi-signature wallets represent one of Bitcoin's most powerful programmable features. These wallets require multiple private keys to authorize transactions, creating shared custody arrangements. For example, a 2-of-3 multi-sig wallet might require any two signatures from three authorized parties to spend funds. This proves invaluable for businesses requiring multiple executive approvals for large transactions, or for personal security where you distribute keys across different locations.
Time-locked transactions add another layer of programmability. Bitcoin supports both absolute time locks (transactions that can't be spent until a specific date) and relative time locks (delays based on block confirmations). Estate planning benefits enormously from this feature. You could create transactions that only become spendable after a certain period, ensuring inheritance distribution according to your wishes.
Advanced Programmable Applications
Bitcoin Script also enables atomic swaps, allowing trustless exchanges between different cryptocurrencies without intermediaries. Hash time-locked contracts create conditional payments that either complete fully or refund automatically, eliminating counterparty risk in cross-chain transactions.
Payment channels form the foundation of the Lightning Network through programmable Bitcoin transactions. These channels lock funds in multi-sig addresses with specific spending conditions, enabling instant off-chain payments while maintaining Bitcoin's security guarantees. The programmability ensures that even if one party becomes unresponsive, funds can still be recovered through automated processes.
How Do You Store Bitcoin Safely?
Bitcoin storage represents one of the most critical aspects of cryptocurrency ownership that every user must understand. Unlike traditional banking, where institutions safeguard your money, Bitcoin operates on the principle of "be your own bank." This places full responsibility for security on individual users.
Understanding Bitcoin Wallets
Bitcoin wallets don't actually store bitcoins. They store the private keys that control access to bitcoins recorded on the blockchain. Think of your wallet as a keychain containing cryptographic keys that prove ownership of specific Bitcoin addresses. Lose these keys? You lose access to your Bitcoin permanently, with no customer service to call for recovery.
Wallets come in several categories, each offering different balances of convenience and security:
- Software wallets - Easy access for frequent transactions but vulnerable to malware and hacking. Popular options include Electrum for desktop users and Blue Wallet for mobile devices.
- Web wallets - Maximum convenience for beginners through internet browsers, but require trusting third parties with private keys. Exchange wallets like Coinbase or Binance fall into this category.
- Hardware wallets - Highest security through specialized devices like Ledger Nano S/X or Trezor models that store keys offline and require physical confirmation for transactions.
- Paper wallets - Basic cold storage with private keys printed on physical paper, immune to digital attacks but requiring careful handling to prevent damage or theft.
Self-Custody Best Practices
Successful Bitcoin self-custody requires following established security practices that have evolved through years of real-world experience. Understanding and implementing these practices protects your investment while maintaining the sovereignty that makes Bitcoin unique.
Seed Phrase Security and Backup
Seed phrases, typically consisting of 12 or 24 randomly generated words, serve as master keys for wallet recovery. These words can restore your entire wallet if your device is lost, stolen, or damaged.
Never store seed phrases digitally or photograph them with cameras connected to the internet. Write them clearly on paper or stamp them into metal plates designed for seed phrase storage. Create multiple copies stored in different physical locations to protect against fire, flood, or other disasters.
Advanced Security Measures
Multi-signature setups provide advanced security by requiring multiple private keys to authorize transactions. A common configuration uses three keys with a 2-of-3 requirement - perhaps one on your phone, one on a hardware wallet, and one in a bank safety deposit box. This protects against single points of failure while maintaining accessibility.
Regular security audits help maintain long-term Bitcoin safety. Test wallet recovery procedures periodically using small amounts to ensure you can actually access your funds when needed. Update software wallets regularly and verify hardware wallet firmware authenticity before installation. For inheritance planning, consider combining multi-signature setups with time-locks to create self-executing wills, ensuring secure generational transfer without intermediaries.
Common Security Threats
Bitcoin users face several categories of security threats requiring different defensive approaches:
- Phishing attacks - Fake websites or emails impersonating legitimate services to steal credentials. Always type wallet URLs manually or use bookmarks rather than clicking links.
- SIM swapping - Attackers convince mobile carriers to transfer your number to their devices, targeting phone-based authentication. Avoid SMS-based 2FA, preferring app-based authenticators or hardware keys.
- Physical threats - Unlike insured bank accounts, stolen Bitcoin rarely gets recovered. Consider operational security, like avoiding public discussion of holdings and using decoy wallets for small amounts.
- Malware and keyloggers - Malicious software designed to steal private keys or wallet passwords from infected devices.
- Social engineering - Scammers impersonating support staff or trusted contacts to trick users into revealing sensitive information.
How Does Bitcoin Compare to Traditional Banking?
Understanding Bitcoin's advantages and limitations requires comparing it directly with traditional financial systems that most people use daily. These systems operate on fundamentally different principles, creating distinct trade-offs for users.
Transaction Processing and Speed
Traditional banks operate as centralized intermediaries that hold customer funds and process transactions through internal ledgers. When you send money to someone, banks update database entries rather than physically moving anything. This centralization enables rapid transaction processing and familiar customer service, but creates single points of failure.
Bitcoin eliminates intermediaries through its peer-to-peer network, where transactions occur directly between users. No bank approves or reverses transactions - the network validates them according to mathematical rules. This trustless system removes reliance on institutions but means no one can help if you make mistakes.
Transaction speed varies significantly between systems. Traditional digital payments appear instant but actually take days to settle through correspondent banking networks. International wire transfers commonly take 3-5 business days and involve multiple intermediary banks. Bitcoin transactions take 10-60 minutes for confirmation on the base layer, though the Lightning Network enables instant payments.
Cost Structure and Access Requirements
Cost structures differ dramatically between systems. Banks generate revenue through hidden spreads, monthly fees, overdraft charges, and various service fees that aren't always transparent. Bitcoin transactions have explicit fees based on network congestion, typically ranging from $1-10 for base layer transactions. Users can choose their fee level based on urgency, with higher fees ensuring faster confirmation.
Access requirements create perhaps the most significant distinction. Traditional banking requires extensive documentation, credit checks, and often minimum balances or geographic restrictions. Millions of people worldwide lack access to banking services due to these barriers. Bitcoin requires only internet access and basic technical knowledge, enabling financial participation for anyone regardless of location or economic status.
Privacy and Transaction Finality
Privacy considerations follow opposite philosophies. Banks collect extensive personal information and monitor all transactions for regulatory compliance, creating detailed financial profiles. Bitcoin offers pseudonymous transactions where addresses aren't directly linked to identities, though blockchain analysis can sometimes trace transaction flows. While Bitcoin's transparency enhances auditability, advanced users employ mixing services or privacy-focused wallets to further enhance pseudonymity, which contrasts with banks' mandatory 'know-your-customer' requirements.
Reversibility represents a fundamental difference in transaction finality. Credit cards and bank transfers can be reversed through chargebacks, disputes, or fraud claims, protecting consumers but enabling certain types of fraud. Bitcoin transactions are irreversible after confirmation, eliminating chargeback fraud but requiring users to exercise greater caution.
What Challenges Does Bitcoin Face?
Despite its revolutionary potential, Bitcoin confronts several significant obstacles that affect its adoption and practical use. Understanding these challenges provides a realistic perspective on Bitcoin's current limitations and future development needs.
Price Volatility
Bitcoin's price movements remain one of its most significant practical challenges for everyday use. Price swings of 20-30% are common in emerging markets like Bitcoin's, though volatility tends to decrease with market maturity and broader institutional adoption. Historical data shows volatility decreasing over time as Bitcoin matures, similar to other asset classes during their development phases.
Scalability Limitations
Bitcoin's transaction processing capacity represents a key technical challenge requiring innovative solutions. The base layer processes approximately 7 transactions per second, far below traditional payment networks. However, Layer 2 solutions like the Lightning Network address this limitation by enabling instant, low-cost micropayments through off-chain channels.
The Lightning Network enables millions of efficient off-chain transactions, demonstrating Bitcoin's scaling potential without compromising security.
Layer 2 Development
Technical innovations continue expanding Bitcoin's practical applications beyond its base layer limitations. Layer 2 solutions address scalability concerns while preserving Bitcoin's security and decentralization properties, creating new possibilities for everyday usage.
Lightning Network Architecture
The Lightning Network operates by creating payment channels between users through multi-signature Bitcoin transactions. Two parties can open a channel by creating a shared wallet, then conduct unlimited transactions off-chain by updating the balance distribution. Only the opening and closing transactions need to be recorded on Bitcoin's main blockchain, dramatically reducing fees and confirmation times.
Lightning's true power emerges through payment routing across networks of channels. You don't need direct channels with everyone - payments can route through intermediate nodes to reach any destination. For example, if Alice has a channel with Bob, and Bob has a channel with Carol, Alice can pay Carol through Bob without opening a direct channel. This creates a mesh network enabling global Bitcoin payments with minimal on-chain footprint.
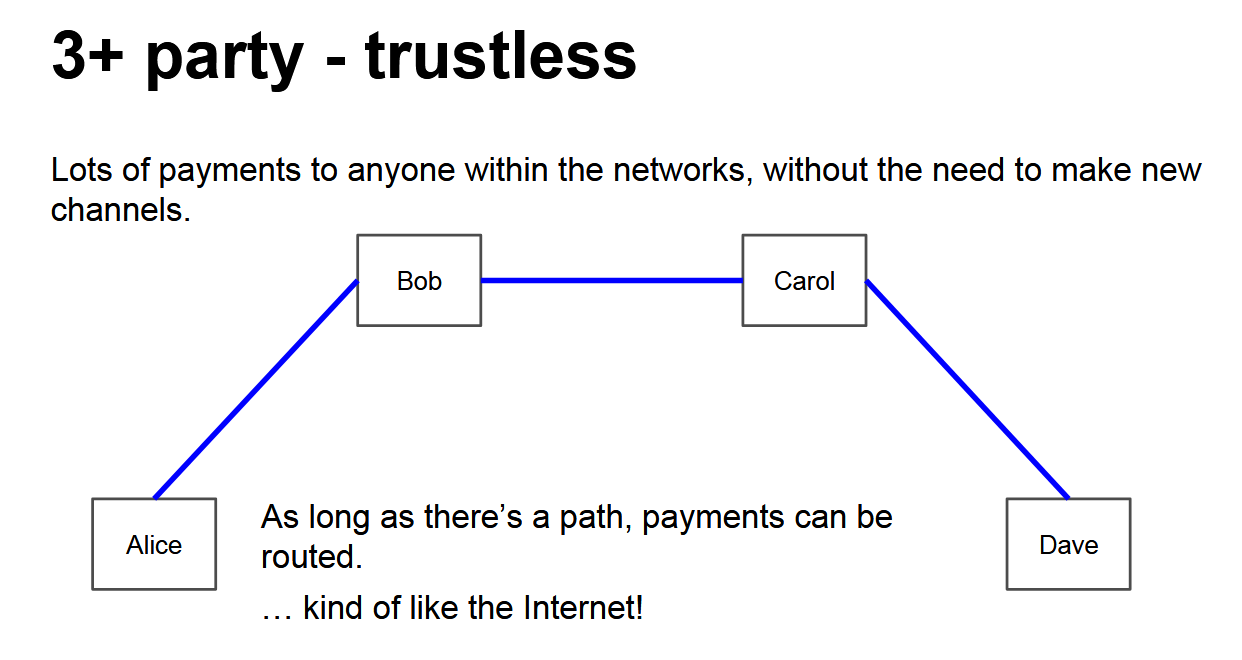
Lightning Network Challenges and Alternatives
Liquidity management represents Lightning's primary challenge. Channels require upfront Bitcoin deposits, and receiving payments depletes your ability to send until you rebalance. Routing nodes earn small fees for facilitating payments but must maintain proper liquidity across multiple channels.
Other Layer 2 innovations include sidechains like Liquid Network, which enables faster settlement for Bitcoin transactions between exchanges and institutions. These alternatives offer different trade-offs between speed, security, and decentralization, expanding Bitcoin's utility for various use cases beyond the Lightning Network's peer-to-peer focus.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The evolving regulatory landscape creates ongoing uncertainty for Bitcoin users and businesses worldwide. Ongoing global variations, from full adoption in some nations to restrictions in others, highlight the need for clear regulatory frameworks as the technology matures. Clearer frameworks could accelerate integration, as seen in jurisdictions treating Bitcoin as property for tax purposes, providing legal certainty for businesses and investors.
Energy Consumption Concerns
Environmental considerations continue to influence public perception and regulatory approaches to Bitcoin. Critics cite Bitcoin's energy usage as environmentally problematic. The industry's shift toward renewable sources and the utilization of stranded energy resources addresses these concerns while incentivizing the development of clean energy.
How is Bitcoin Adoption Evolving?
Bitcoin's mainstream acceptance has accelerated dramatically, with institutional and retail adoption reaching new milestones. Several key trends demonstrate Bitcoin's growing integration into traditional financial systems.
Institutional Investment Surge
Corporate and institutional demand for Bitcoin has reached unprecedented levels. Institutions increasingly view Bitcoin as a treasury asset superior to cash for long-term preservation, with ETFs and corporate holdings driving sustained demand. Beyond corporations, pension funds and sovereign wealth funds increasingly allocate to Bitcoin, viewing it as a diversification tool against fiat debasement and monetary policy uncertainty.
Major corporations now hold Bitcoin on balance sheets as a treasury reserve asset, viewing it as superior to cash for long-term value preservation.
Geographic Expansion
Global Bitcoin adoption patterns reveal increasing usage in regions facing monetary instability. In emerging markets, Bitcoin's mobile-first accessibility drives remittances, with volumes often surpassing traditional channels in high-inflation zones. Citizens in countries experiencing currency devaluation or capital controls increasingly turn to Bitcoin for financial stability.
Hyperinflation Use Cases
Real-world adoption stories illustrate Bitcoin's practical impact in countries facing severe monetary challenges. In Venezuela, where hyperinflation has destroyed the bolivar's purchasing power, citizens use Bitcoin for financial preservation. Local businesses accept Bitcoin payments, and peer-to-peer trading volumes consistently rank among the world's highest despite government restrictions.
Nigerian users have embraced Bitcoin amid currency restrictions and inflation concerns. Peer-to-peer Bitcoin trading volumes in Nigeria consistently exceed those of many developed nations, as users seek alternatives to traditional banking limitations.
Government Adoption Models
El Salvador's adoption of Bitcoin as legal tender represents the most significant governmental embrace of cryptocurrency. The country's ongoing Bitcoin treasury strategy while enabling citizen usage provides valuable data on Bitcoin's potential as a national currency. This experiment demonstrates both the opportunities and challenges of sovereign Bitcoin adoption in practice.
How Does Bitcoin Compare to Other Cryptocurrencies?
Bitcoin's position as the first and largest cryptocurrency often leads to comparisons with newer blockchain projects that promise different features or improvements. Understanding these differences helps clarify Bitcoin's unique value proposition and design trade-offs.
Ethereum and Smart Contract Platforms
Ethereum represents Bitcoin's most significant competitor, though it serves different primary purposes. While Bitcoin focuses purely on being digital money, Ethereum operates as a platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications. Ethereum switched from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake consensus, dramatically reducing energy consumption but introducing different security assumptions.
Proof-of-stake systems like Ethereum secure networks through economic stake rather than energy expenditure. Validators must deposit cryptocurrency as collateral, losing funds if they validate incorrect transactions. This approach uses far less energy but potentially concentrates power among wealthy stakeholders who can afford large deposits.
Bitcoin's proof-of-work deliberately ties security to external energy expenditure, ensuring attackers must invest real-world resources rather than cryptocurrency holdings. This creates stronger immutability guarantees but requires ongoing energy consumption.
Network Effects and Competitive Advantages
Bitcoin has created substantial competitive advantages that newer projects struggle to overcome. Understanding these network effects helps explain Bitcoin's continued dominance despite technical innovations from competitors.
Technical and Economic Trade-offs
Transaction speed and fees vary significantly across cryptocurrencies. Newer blockchains often achieve faster transaction processing and lower fees by making different trade-offs in decentralization or security. However, these systems typically have fewer nodes and less battle-tested security than Bitcoin's network.
Monetary policies differ substantially between cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin's fixed 21 million coin supply contrasts with Ethereum's variable issuance or other projects' inflationary tokenomics. Many altcoins allocate significant percentages to founders or foundations, unlike Bitcoin's fair launch, where Satoshi mined under the same rules as everyone else.
Network Effects and Market Position
Network effects and adoption create significant competitive advantages that compound over time. Bitcoin benefits from first-mover advantage, widespread recognition, regulatory clarity in many jurisdictions, and the largest ecosystem of supporting infrastructure. Bitcoin's robust network effects and proven security provide stronger foundations than newer projects, which often prioritize speed or features over battle-tested reliability.
Stablecoins serve different functions by pegging values to fiat currencies like the US dollar. These provide crypto's technical benefits while maintaining price stability, making them useful for payments and trading. However, their pegs tie them to fiat risks and monetary policy decisions, unlike Bitcoin's independent monetary policy and finite supply schedule.
What Does Bitcoin's Future Hold?
Bitcoin's long-term trajectory appears increasingly positive as technological improvements and institutional acceptance converge. Several factors suggest continued growth and development in the coming years.
Price Predictions and Market Cycles
Historical patterns and current market dynamics suggest Bitcoin may continue following predictable growth cycles. Bitcoin's four-year halving cycles historically drive appreciation, with experts anticipating continued growth from supply reduction and increasing demand catalysts.
Factors like regulatory clarity, geopolitical shifts toward hard assets, institutional integration, and technological upgrades position Bitcoin for expanded roles in global finance. However, market cycles remain inherently unpredictable despite historical patterns.
Technical Development
Bitcoin's core protocol continues evolving through careful, consensus-driven improvements that enhance functionality without compromising security. Ongoing development focuses on privacy enhancements, efficiency improvements, and expanded programmability while maintaining the network's foundational security properties.
Emerging enhancements like Schnorr signatures improve privacy and efficiency by enabling signature aggregation and reducing transaction sizes. Meanwhile, innovations like Ordinals enable NFT-like functionality on Bitcoin's base layer, demonstrating the protocol's adaptability for new use cases while preserving its core monetary properties.
Global Financial Integration
The integration of Bitcoin into traditional financial infrastructure represents a significant long-term trend. As Bitcoin infrastructure matures, integration with traditional financial systems deepens. Banks offer Bitcoin custody services, payment processors accept Bitcoin payments, and governments explore Bitcoin reserves.
Potential central bank digital currency (CBDC) coexistence could see Bitcoin serving as a neutral reserve asset, bridging traditional and decentralized finance systems. This integration reflects Bitcoin's growing recognition as legitimate digital infrastructure rather than speculative technology.
Conclusion
Bitcoin, a fundamental transformation in monetary technology, combining the scarcity of gold with the efficiency of digital systems. Its decentralized architecture, cryptographic security, and fixed supply schedule create a unique asset class that challenges traditional financial assumptions.
With institutional adoption accelerating and technical infrastructure improving, Bitcoin's role in the global financial system continues expanding. While challenges like volatility and regulatory uncertainty persist, Bitcoin's fundamental properties - scarcity, decentralization, and censorship resistance - position it as a significant force in finance's digital future.
Whether viewed as digital gold, a hedge against inflation, or a technological breakthrough, Bitcoin has established itself as a permanent fixture in the financial landscape. Understanding its mechanics, benefits, and limitations enables informed decisions about participation in this revolutionary monetary system.
Become your own bank, start your journey at bitcoin.org.
Recent Bitcoin Coverage:
- Bitcoin Recent Updates: Institutions, Banks, and Treasuries Deepen Their Role
- Coinbase Introduces Bitcoin-Back Rewards Card for U.S. Users
- Sora Ventures Reveals Plan for Asia’s First $1B Bitcoin Treasury Fund
- Indonesia Explores Bitcoin as Reserve Asset to Boost Economy
- Michael Saylor's Strategy Buys 21021 Bitcoin in 'Largest US IPO' of 2025
Spanish Coffee Chain Aims to Become Spain’s Biggest Bitcoin Treasury With $1B+
Sources
- bitcoin.org - Nakamoto, S. (2008). Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System. (Whitepaper)
- Blockchain.com Bitcoin Network Statistics. (2025).
- CoinMarketCap - Historical data
- Bloomberg - Bitcoin ETF Data
- Wikipedia - Proof of Work, Lightning Network, and Merkle Trees
- 1ML - Lightning Network Statistics
- Cambridge - Bitcoin Energy Consumption Index
- Chainalysis - Bitcoin strategic reserves
- Bitcoin.org - Technical Documentation
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I buy Bitcoin safely?
Purchase Bitcoin through reputable exchanges like Coinbase, Kraken, or Binance. Transfer coins to a hardware wallet for long-term storage, never leaving large amounts on exchanges. Verify wallet addresses carefully and use two-factor authentication on all accounts.
Can Bitcoin be hacked or shut down?
Individual wallets can be compromised through poor security practices, but the Bitcoin network itself has never been successfully attacked. Its decentralized nature across thousands of nodes makes network shutdown practically impossible.
Is Bitcoin legal?
Bitcoin legality varies by jurisdiction. Most developed countries treat it as a commodity or property for tax purposes. While some nations restrict or ban Bitcoin, enforcement remains challenging due to its decentralized nature.
How much Bitcoin should I own?
Financial advisors typically recommend 1-5% portfolio allocation to Bitcoin as a high-risk, high-reward asset. Never invest more than you can afford to lose, as cryptocurrency markets remain highly volatile.
Will Bitcoin replace traditional money?
Bitcoin serves more as "digital gold" than daily spending money due to volatility and transaction costs. It complements rather than replaces fiat currencies, offering an alternative store of value and inflation hedge.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens




















