Internet Computer & ICP: Building a Decentralized Internet

The Internet Computer (ICP) offers a decentralized alternative to cloud services, enabling developers to build applications directly on the blockchain without traditional IT infrastructure. Learn how this layer-1 protocol works to create a truly decentralized internet.
Crypto Rich
April 21, 2025
Table of Contents
What Is the Internet Computer Protocol?
The Vision of a Decentralized Web
The Internet Computer (ICP) is a layer-1 blockchain protocol that functions as a "World Computer" – enabling developers to build and run complete web applications directly on the blockchain without relying on traditional cloud services like Amazon Web Services or Google Cloud. Unlike conventional blockchains that only handle small parts of applications, ICP allows both front-end interfaces and back-end logic to run entirely on-chain, creating truly decentralized applications where users don't pay transaction fees. Launched in May 2021 by the Swiss not-for-profit DFINITY Foundation, the Internet Computer creates a decentralized network of independent data centers running specialized hardware nodes, organized into subnets that function as independent blockchains.
Beyond Traditional Blockchain Applications
What makes ICP different is its focus on hosting complete web applications. When you use a typical blockchain app today, only small parts actually run on the blockchain. The Internet Computer changes this by allowing both the front-end interface and back-end logic to run entirely on-chain, meaning the whole application lives on the blockchain.
The Internet Computer stands out through several key innovations:
- Decentralized Architecture: A network of independent data centers running specialized hardware nodes, organized into subnets that function as independent blockchains.
- Canister Smart Contracts: Self-contained units storing both code and state – essentially tiny virtual computers running full applications.
- Chain Key Cryptography: Technology creating secure digital signatures across blockchains, allowing direct interaction without intermediaries.
- Reverse Gas Model: A system where developers pay for computation while users access applications for free.
This architecture enables ICP applications to interact with other blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum directly and securely. The enhanced Chain Key TX functionality (transaction capability across chains) means ICP smart contracts can directly create and sign transactions on other blockchains. The native Ethereum integration via Chain Key TX is partially live, with key components like ckETH, ckERC-20, and the EVM RPC canister enabling significant interoperability. However, the full integration, eliminating all dependencies on external providers and supporting all Ethereum protocols, remains under active development. For Bitcoin, this integration allows applications like Bitcoin DeFi where ICP canisters can hold and transfer actual BTC without risky bridge technologies.
The Unique Economic and Governance Model
Rethinking Blockchain Economics
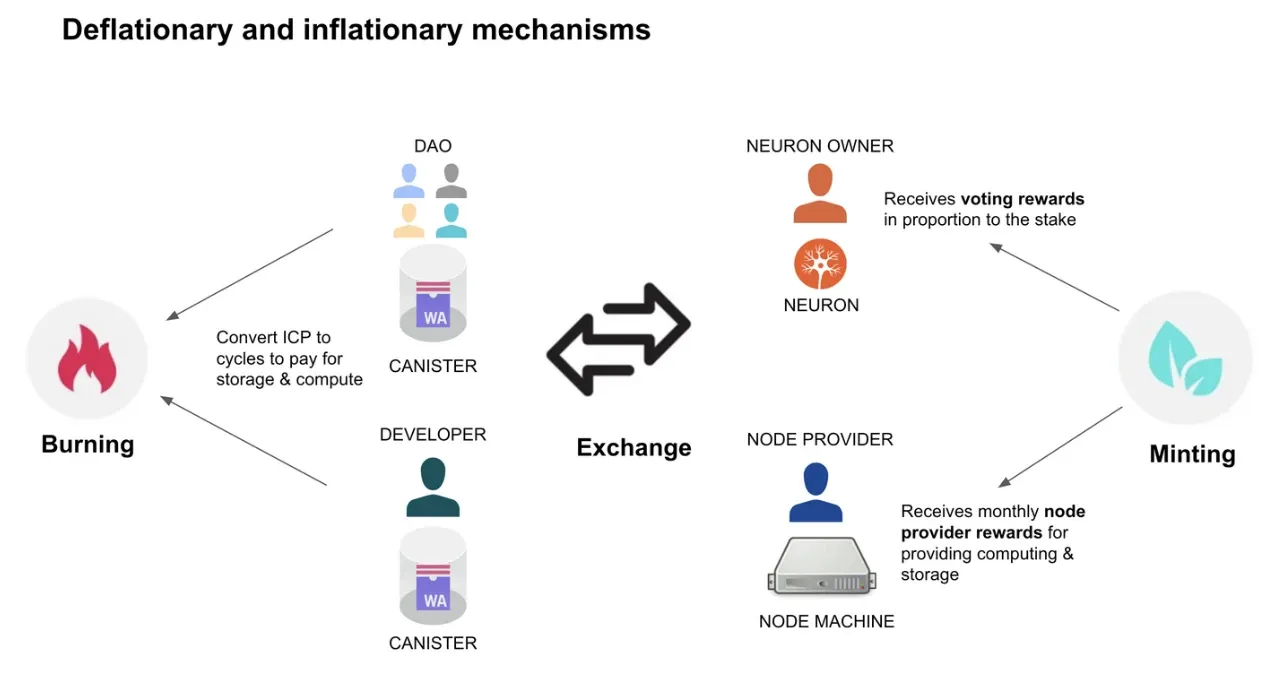
Most blockchains require users to pay fees (gas) for every action. This works for financial transactions but creates friction for everyday applications. The Internet Computer solves this with its "reverse gas model." Developers pay for computation by converting ICP tokens into "cycles" – a stable unit pegged to the Swiss Franc. These cycles fund application operation, similar to how a business pays for server costs rather than charging visitors per click.
When developers deploy an ICP application, they attach a cycle wallet with enough funds to keep it running. Users can then interact with these applications without needing cryptocurrency or paying transaction fees.
Community-Driven Governance
The Internet Computer's governance operates through the Network Nervous System (NNS), an on-chain DAO (Decentralized Autonomous Organization) that manages the network through voting. The NNS handles everything from technical upgrades to economic policy through transparent on-chain voting.
Token holders participate by staking their ICP in voting "neurons" that give them decision-making power. The longer they commit to staking, the more voting power they receive, encouraging long-term thinking over short-term profit-seeking.
To make applications more user-friendly, ICP includes a privacy-focused authentication system called Internet Identity. Users can log in securely using biometrics (like fingerprint or facial recognition) or security keys instead of passwords, creating a seamless experience while preventing cross-site tracking. This system generates unique anonymous credentials for each application, enhancing both security and privacy without the complexity typical of blockchain interactions.
While the DFINITY Foundation currently holds significant ICP tokens, which give it substantial voting power, its governance roadmap includes plans to progressively reduce this influence over time through broader token distribution and encouraging more community participation in the NNS.
The Multi-Purpose ICP Token
The ICP token serves multiple functions within this ecosystem:
- Governance Participation: Staked tokens allow voting on proposals that shape the network's future
- Computation Funding: Developers burn ICP to create cycles that keep their applications running
- Node Provider Payments: Data centers powering the network receive compensation based on their operational costs
- Decentralization Swaps: Projects can transfer control to their communities through "SNS" launches
These economic mechanisms create both inflationary forces (through rewards to stakers and node providers) and deflationary pressures (through token burning for cycles). According to community sources, after June 2025, when scheduled token unlocks cease, the overall trend may shift toward deflation if application usage continues to grow.
The Growing Ecosystem and Recent Developments
Technical Advancements
The Internet Computer has transformed from its initial promise into a robust, functioning ecosystem with significant technical developments. Recent advancements have substantially expanded its capabilities and use cases.
ICP Ninja now simplifies blockchain development through a web-based environment that reduces setup time from days to minutes. Additionally, the platform's Chain Key TX system has advanced, allowing smart contracts on ICP to directly create and sign transactions on Bitcoin – eliminating the need for vulnerable cross-chain bridges that have lost billions in hacks.
Running an Internet Computer node requires substantial resources – currently 16-core processors, 128GB RAM, and 2TB NVMe storage at minimum, with costs starting around $1,500 per month for hardware and data center expenses. This high requirement enables performance needed for web applications but restricts who can participate in the network infrastructure.
Ecosystem Growth
The network now hosts diverse applications across several categories:
- Finance: ICDex operates as the first fully on-chain, orderbook-based decentralized exchange, while OISY Wallet provides multi-chain custody without requiring users to manage complex private keys
- Social Media: Yral offers a decentralized video platform where content cannot be arbitrarily removed, while Nuance provides bloggers with true ownership of their content
- Developer Tools: Juno simplifies Web3 development by providing familiar interfaces for developers accustomed to traditional web development
- Governance Solutions: Orbit Platform enables teams to create customized governance systems for managing digital assets collectively
Emerging Focus Areas
ICP has positioned itself at the intersection of blockchain and artificial intelligence. Projects are building AI applications that run entirely on-chain, making them resistant to censorship or control by any single entity. Kinic deploys AI tooling, including vector databases and machine learning models, directly on ICP, creating applications that continue running exactly as programmed.
Furthermore, the Internet Computer community has made environmental sustainability a core focus. Through NNS Proposal No. 55487, the network established comprehensive sustainability policies that led to significant progress. The Internet Computer Footprint project reported a 32% reduction in carbon emissions during 2024 by optimizing data center operations and transitioning several node providers to renewable energy sources. These concrete results demonstrate that blockchains can address environmental concerns while maintaining decentralization, making ICP an attractive option for environmentally conscious developers and users.
Challenges and Future Direction
Addressing Controversies and Centralization Concerns
The Internet Computer's 2021 launch was not without controversy. Reports from CryptoLeaks alleged market manipulation and coordination between certain parties to drive down ICP's price after its initial listing. DFINITY strongly denied these allegations, emphasizing the transparent nature of the NNS governance system and pointing to market-wide crypto downturns during that period. It's worth noting that independent verification of CryptoLeaks' claims is lacking. These discussions highlight the challenges of token distribution and price stability that many blockchain projects face at launch.
Critics also point to centralization issues, noting that the DFINITY Foundation's significant ICP holdings could potentially give it outsized influence over governance decisions. While the Network Nervous System allows anyone with sufficient ICP to participate in governance, voter turnout and token distribution still skew power toward larger holders. The high hardware requirements for nodes – estimated to start around $1,500 monthly to operate, though costs may vary based on location, hosting method, and hardware vendor – further limit who can participate in the network's infrastructure.
The DFINITY Foundation has acknowledged these concerns and outlined plans to gradually decentralize control through broader token distribution and enhanced community governance mechanisms.
Technical Learning Curve
The technical learning curve presents another challenge. Developers must learn new programming languages like Motoko or adapt to ICP's unique implementation of Rust. The canister model differs significantly from traditional smart contract platforms, requiring a different approach to application development.
Documentation and tooling continue to improve but remain less mature than older blockchain ecosystems, presenting barriers to adoption for some developers.
The Road Ahead
Looking forward, the Internet Computer's roadmap focuses on several key areas:
- Cross-Chain Integration: Expanding Chain Key TX functionality to connect with more blockchain networks
- Developer Experience: Improving tools and documentation to lower the barrier to entry
- AI Infrastructure: Developing capabilities for hosting decentralized AI applications
- Scaling: Increasing the number of subnets and nodes to enhance network capacity globally
These priorities will be highlighted at the Global R&D event in March 2025, which will focus on updates to the ICP roadmap and developer tools. The event represents a significant milestone for showcasing ICP's technical progress and future direction to the broader blockchain community.
The Neon Milestone, set for June 2025, aims to streamline SNS launches and enhance NNS governance, encouraging broader community participation.
Community initiatives like hackathons and the "Reimagining the Internet" forum aim to expand the developer community beyond those already familiar with blockchain technology.

Conclusion: Building a More Open Internet
The Internet Computer represents an ambitious attempt to reimagine internet infrastructure through blockchain technology. By enabling fully on-chain applications with user-friendly interfaces, ICP aims to create digital services that cannot be censored, shut down, or controlled by centralized entities.
This vision addresses growing concerns about the power of tech giants over our digital lives. While challenges remain in achieving full decentralization, simplifying development, and driving mainstream adoption, the Internet Computer's technical approach offers capabilities that weren't previously possible on blockchains.
The question now is whether enough people will choose to build and use these decentralized alternatives to shift the internet toward a more open future. For those concerned about the current trajectory of the web, the Internet Computer offers not just criticism of existing systems, but a working alternative already in motion.
To explore the Internet Computer ecosystem further, visit the official website at internetcomputer.org and follow @dfinity on Twitter for the latest developments, community events, and technical updates.
Sources
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the Internet Computer differ from other blockchains like Ethereum?
The Internet Computer enables complete web applications to run entirely on-chain, including front-end interfaces and back-end logic, while most blockchains only handle small application components. It uses a "reverse gas model" where developers pay for computation through cycles, allowing users to access applications for free without cryptocurrency or transaction fees.
What are ICP tokens used for and how do they work?
ICP tokens serve multiple purposes: governance participation through staking in voting neurons, funding application computation by converting to cycles, compensating node providers, and enabling decentralized project launches through SNS swaps. The token economics create both inflationary forces through rewards and deflationary pressures through token burning for cycles.
Can Internet Computer applications interact with Bitcoin and Ethereum?
Yes, through Chain Key TX functionality, ICP smart contracts can directly create and sign transactions on other blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum without risky bridge technologies. For Bitcoin, this enables applications like DeFi where ICP canisters can hold and transfer actual BTC, while Ethereum integration includes ckETH, ckERC-20, and EVM RPC canister support.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens
Latest Crypto News
Get up to date with the latest crypto news stories and events


















