What is Ethereum (ETH) and How Does it Work?
Learn what Ethereum is, how smart contracts work, and why ETH powers DeFi and Web3. Complete 2025 guide to blockchain's programmable platform.
Crypto Rich
February 4, 2025
Table of Contents
Ethereum is a decentralized blockchain platform that has become the foundation for modern Web3 applications. Unlike simple digital currencies, Ethereum enables smart contracts and decentralized applications that run exactly as programmed. As the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization after Bitcoin, it transformed blockchain from basic payments into a programmable computing platform.
Since launching in 2015, Ethereum has grown from an experimental project into the backbone of decentralized finance. Today, the platform processes billions in transactions daily while hosting thousands of applications that operate without traditional intermediaries.
How Did Ethereum Begin and Who Created It?
The story of Ethereum begins with Vitalik Buterin, a young programmer who saw bigger possibilities for blockchain technology. As a Bitcoin Magazine co-founder in 2013, he envisioned a platform that could do far more than process digital payments. Buterin's whitepaper proposed something ambitious: a blockchain that could execute programmable smart contracts and host entire decentralized applications.
The idea quickly attracted talented co-founders. Charles Hoskinson (later founder of Cardano), Gavin Wood (who created Polkadot), and Joseph Lubin (founder of ConsenSys) joined the project. After raising $18 million in a crowdfunding campaign, Ethereum launched on July 30, 2015, introducing the world to both its platform and native cryptocurrency, Ether (ETH).

Key Milestones in Ethereum's Development
The platform's evolution follows a clear timeline of major achievements:
- 2013: Vitalik Buterin publishes whitepaper proposing a "world computer" for decentralized applications.
- 2015: Frontier mainnet launches with basic functionality.
- 2016: The DAO hack leads to controversial hard fork, creating Ethereum Classic.
- 2020: Beacon Chain launches, beginning proof-of-stake testing phase.
- 2022: The Merge completes transition to proof-of-stake consensus.
- 2023: Shanghai upgrade enables staked ETH withdrawals.
- 2024: Dencun upgrade introduces proto-danksharding for cheaper Layer-2 transactions.
- 2025: Pectra upgrade enhances wallet functionality and staking efficiency (May 7).
This progression shows Ethereum's commitment to continuous improvement. The network maintains security and decentralization while evolving its capabilities.
What Makes Ethereum Different from Bitcoin?
Bitcoin and Ethereum tackle different challenges in the cryptocurrency world. Bitcoin excels as digital gold - a secure store of value that prioritizes security over complexity. Ethereum takes a different approach, serving as a global computing platform where developers build applications that run without traditional servers or intermediaries.
The key difference lies in programmability. While Bitcoin handles straightforward transactions, Ethereum can execute complex logic through smart contracts.
Smart Contracts: The Core Innovation
Smart contracts are programs that run automatically when specific conditions are met. Think of them as digital agreements that execute themselves - no lawyers, no paperwork, no waiting for someone to process your request.
Here's how they work: these contracts run on the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), which processes instructions across thousands of computers worldwide. When you buy something online and the smart contract detects your payment, it automatically releases the digital goods to your wallet. The seller gets paid, you get your purchase, and neither party needed to trust the other.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine Explained
The EVM is Ethereum's global computer - a virtual machine that runs on thousands of computers simultaneously. Every transaction and smart contract interaction gets processed through this system, ensuring everyone agrees on what happened.
What makes this secure is isolation. Smart contracts run in a sandboxed environment where they can't access your computer's files or network. This prevents malicious code from spreading while keeping the entire system predictable and secure.
How Does Ethereum's Proof-of-Stake System Work?
September 2022 marked Ethereum's biggest transformation yet. "The Merge" successfully transitioned the network from Bitcoin-style mining to a more efficient system called proof-of-stake. This wasn't just a technical upgrade - it cut Ethereum's energy consumption by 99.95% while maintaining the security that users depend on.
Here's what changed: instead of powerful computers competing to solve puzzles (like Bitcoin mining), Ethereum now relies on validators who stake their own ETH to secure the network. Validators need at least 32 ETH to participate directly, though anyone can join through staking pools. The system works because validators have skin in the game - they lose money if they try to cheat.
How Validators Secure the Network
The proof-of-stake system randomly selects validators to propose new blocks and verify others' work. Honest validators earn rewards, while those who misbehave face "slashing" - automatic penalties that can cost them significant ETH. This creates powerful incentives for good behavior.
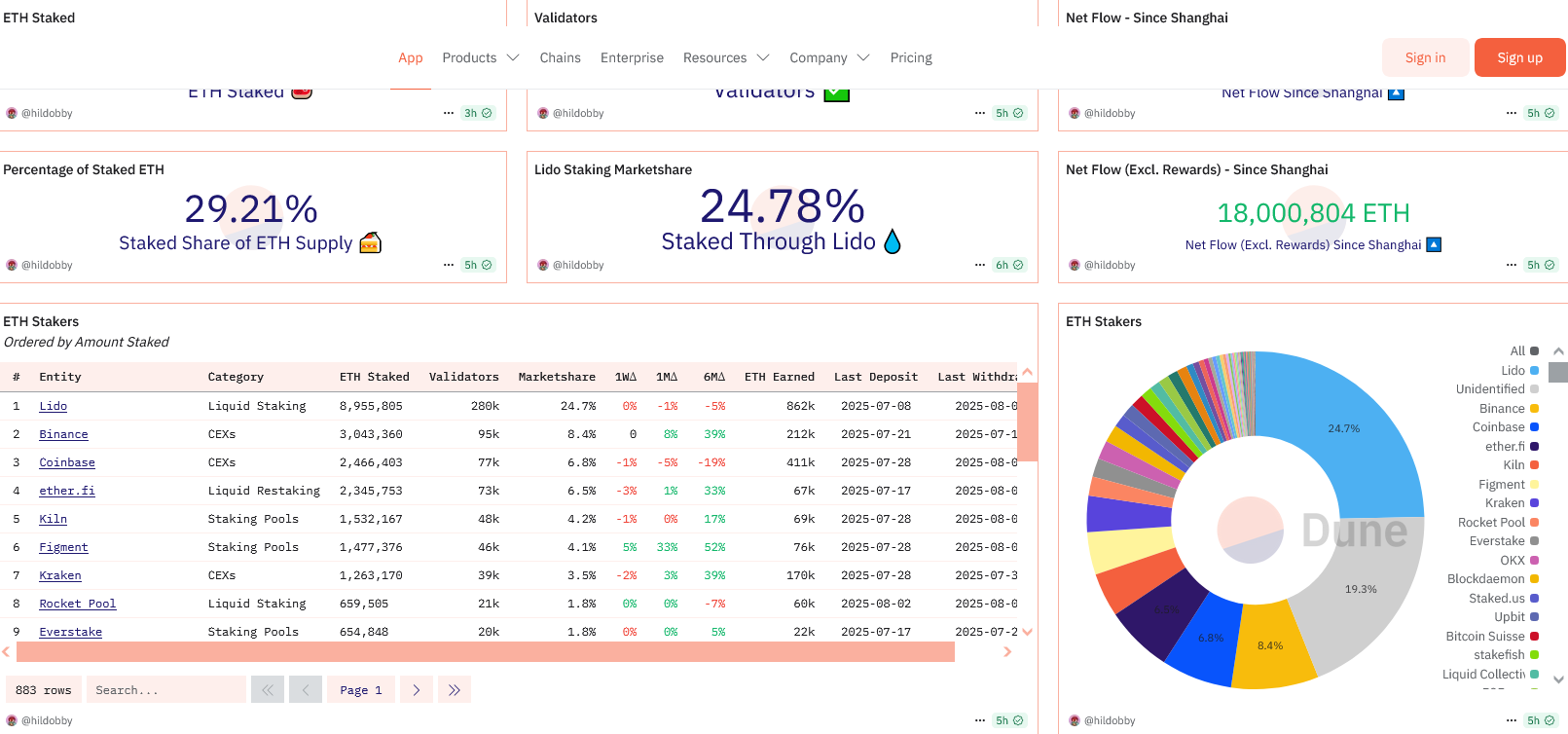
With over 1.05 million validators now securing the network (as of August 2025), coordinated attacks become extremely expensive and difficult to execute. The system delivered impressive results after The Merge:
- Environmental Impact: Energy use dropped by 99.95%, silencing environmental criticism.
- Economic Security: Validators stake their own ETH, aligning financial incentives with network health.
- Accessibility: Anyone can participate without expensive mining equipment.
What Role Does ETH Play in the Ethereum Network?
$ETH serves multiple roles within the Ethereum ecosystem. Think of it as the fuel that powers the entire network.
Users pay ETH for transaction fees, validators stake it for network security, and developers use it to interact with applications. The token operates as the network's economic foundation through several key mechanisms.
Primary Functions of ETH
- Transaction Fees (Gas): Users pay ETH to process transactions and execute smart contracts, with fees varying based on network demand
- Validator Staking: Network validators must stake 32 ETH to participate in consensus and earn rewards
- Store of Value: ETH serves as a digital asset that can be held as investment
- Network Utility: Required for interacting with decentralized applications and DeFi protocols
Token Economics and Supply Dynamics
ETH's economics have evolved significantly since the network's early days. Approximately 120.7 million ETH currently circulates (as of August 2025), with new tokens created through staking rewards.
However, every transaction burns some ETH through EIP-1559, creating deflationary pressure during busy periods. Whether ETH becomes inflationary or deflationary depends on network activity - more usage means more burning.
Understanding Gas Fees and Network Economics
Ethereum uses "gas" to prevent spam and manage network resources efficiently. Every transaction requires gas fees paid in ETH. Since 2021's London upgrade, these fees get partially burned rather than going entirely to validators.
The fee structure splits into two parts:
- Base fee: Gets burned, reducing ETH supply.
- Priority tip: Rewards validators for processing transactions.
For ETH holders who stake their tokens, this creates yields typically ranging from 2-3% annually (August 2025 rates), though rates fluctuate based on network activity and total staked amount.
Why Are Ethereum's Recent Network Upgrades Important?
Ethereum's development never stops. The team continuously ships upgrades that make the network faster, cheaper, and more user-friendly. Each improvement builds on previous work, following a clear roadmap with specific goals.
Major 2024-2025 Upgrades
Recent upgrades have focused on reducing costs and improving user experience:
Dencun Upgrade (March 2024): This introduced "blobs" - a technical improvement that dramatically cut costs for Layer-2 networks like Optimism and Arbitrum. Users now enjoy much cheaper transactions when using these scaling solutions.
Pectra Upgrade (May 7, 2025): This upgrade brought account abstraction to mainstream users, allowing them to pay gas fees with any token and batch multiple transactions together. It also raised the validator staking limit from 32 ETH to 2,048 ETH and increased blob capacity for even lower fees.
Future Development Roadmap
The roadmap ahead looks ambitious:
Fusaka (November 2025): Will introduce PeerDAS (Peer Data Availability Sampling), making data handling more efficient and reducing Layer-2 costs further. This upgrade will also enable mobile devices to participate in staking.
Verkle Trees (2026): This upgrade will shrink the data requirements for running Ethereum nodes, making the network more accessible to everyday users.
Long-term Vision: Ethereum aims to handle over 100,000 transactions per second through Layer-2 scaling while keeping the base layer secure and decentralized.
Which Applications Can You Build on Ethereum?
Ethereum has become the go-to platform for developers building the next generation of internet applications. The network hosts over 4,000 active applications across multiple industries (as of August 2025), proving that decentralized technology can work at scale.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi represents Ethereum's biggest success story. These applications recreate traditional banking services without the banks, offering users more control and often better rates:
- Lending Protocols: Platforms like Aave and Compound let you lend crypto and earn interest, or borrow against your holdings
- Decentralized Exchanges: Uniswap and SushiSwap enable direct peer-to-peer trading without centralized intermediaries
- Stablecoins: USDC, DAI, and similar tokens provide stable value while remaining fully digital
- Yield Farming: Users earn rewards by providing liquidity that keeps these protocols running smoothly
Non-Fungible Tokens and Digital Assets
Ethereum pioneered the NFT revolution through standards like ERC-721 and ERC-1155. These tokens proved that digital ownership could work, creating entirely new markets:
- Digital Art: Platforms like OpenSea turned digital creativity into a tradeable asset class
- Gaming Assets: Players now truly own their in-game items and can trade them across different games
- Virtual Real Estate: Digital land in metaverse platforms has become a legitimate investment category
- Identity and Credentials: Digital certificates and verification systems built on blockchain provide tamper-proof credentials
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations
DAOs represent a new way to organize and make decisions. These token-based organizations let communities govern themselves without traditional corporate structures:
- Protocol Governance: Token holders vote on how protocols develop and spend their treasuries
- Investment DAOs: Groups pool resources to make collective investment decisions
- Creator DAOs: Communities form around supporting artists, writers, and other creators
- Service DAOs: Organizations provide specialized services through decentralized coordination
How Does Ethereum Compare to Other Blockchains?
Ethereum's position in the blockchain space becomes clearer when compared to its main competitors. Each platform made different trade-offs, and understanding these helps explain why Ethereum maintains its leading position.
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
The Bitcoin-Ethereum comparison reveals two different philosophies:
Bitcoin chose to be digital gold - ultra-secure, simple, and focused on storing value. Its proof-of-work system prioritizes security above all else, even if transactions are slower and more expensive.
Ethereum opted for programmability and innovation. Its proof-of-stake system balances security with energy efficiency, enabling thousands of applications while maintaining decentralization.
Ethereum vs. High-Speed Alternatives
Several newer blockchains have tried to challenge Ethereum by offering faster transaction speeds:
Solana can process thousands of transactions per second at very low costs, but achieves this through a more centralized validator structure. While impressive on paper, Solana has experienced several network outages that highlight the trade-offs involved.
Cardano takes a research-first approach, using peer-reviewed development and proof-of-stake like Ethereum. However, it has struggled to build the same ecosystem of applications and developers.
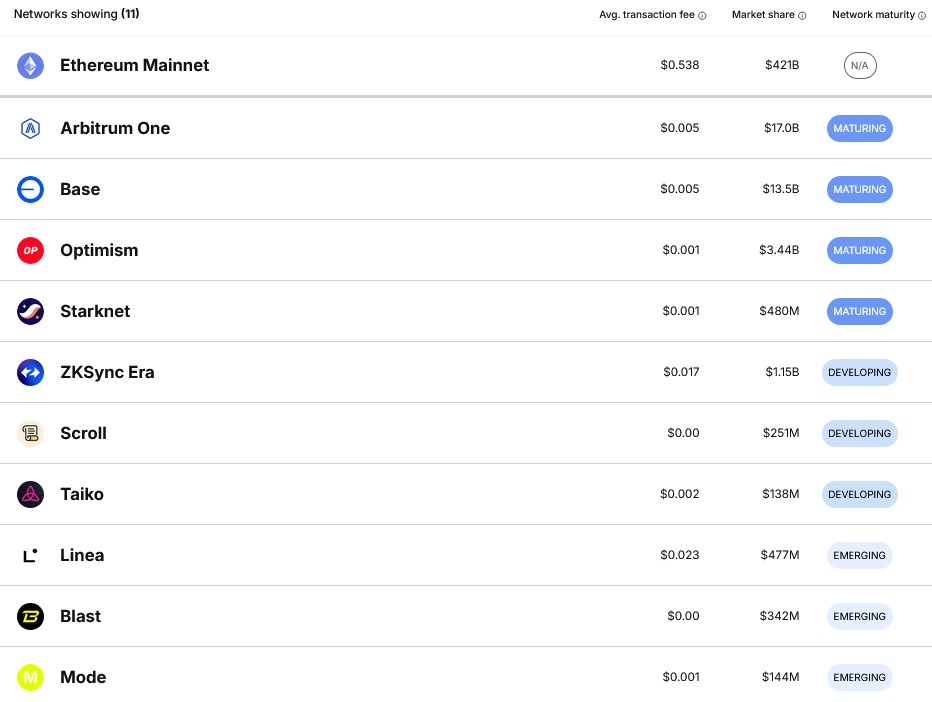
Ethereum's Response: Rather than competing directly on speed, Ethereum focuses on Layer-2 solutions that achieve high throughput while inheriting the base layer's security and decentralization.
Layer-2 Scaling Solutions
Ethereum solves its scalability challenge through Layer-2 networks that process transactions off the main chain while inheriting its security. This approach has proven highly effective:
- Optimistic Rollups: Networks like Optimism and Arbitrum assume transactions are valid unless someone challenges them
- Zero-Knowledge Rollups: Polygon zkEVM and Starknet use mathematical proofs to verify transaction validity instantly
- State Channels: Enable instant, private transactions between specific parties
These solutions now handle the majority of Ethereum's transaction volume while keeping costs low.
What Are the Main Risks When Using Ethereum?
While Ethereum's protocol-level security is robust, users need to understand the risks they face when interacting with the ecosystem. Most security issues stem from user error or application bugs rather than fundamental network problems.
Protocol Security
Ethereum's proof-of-stake design creates strong security through economic incentives:
Validator Penalties: Validators lose money for dishonest behavior or going offline too long, aligning their interests with network health.
Massive Decentralization: Over 1.05 million validators secure the network (as of August 2025), making coordinated attacks extremely expensive and difficult to execute.
Common User Risks and Mitigation
Despite strong network security, users face several common risks:
Smart Contract Bugs: Code errors can lead to lost funds. Research protocols thoroughly and start with small amounts when trying new applications.
Phishing and Scams: Fake websites and social media accounts try to steal your private keys or trick you into malicious transactions. Double-check URLs and never share your seed phrase with anyone.
Wallet Security: Your private keys are your responsibility. Use hardware wallets for large amounts, enable two-factor authentication when available, and regularly review your token approvals.
Best Practices for Safe Interaction
Smart security practices protect you from most risks:
- Keep wallet software updated and use reputable providers
- Verify smart contract addresses before interacting
- Set spending limits and regularly clean up old token approvals
- Never share private keys or seed phrases
- Stay skeptical of investment opportunities that seem too good to be true
What Challenges Does Ethereum Face?
Like any technology, Ethereum faces ongoing challenges. The good news is that the development community actively works on solutions, and many improvements are already showing results.
Scalability and Transaction Costs
Ethereum's base layer can only handle about 15 transactions per second, which causes congestion during busy periods. High gas fees during these times can make small transactions uneconomical.
Current Solutions: Layer-2 rollups already provide much higher throughput and lower costs while maintaining the security of the main chain.
Future Improvements: Upcoming upgrades will make Layer-2 networks even cheaper and more efficient.
User Experience Complexity
Using Ethereum still requires understanding concepts like gas fees, private keys, and smart contract interactions. This complexity can intimidate newcomers.
Ongoing Improvements: Account abstraction features in recent upgrades are making wallets much more user-friendly, enabling gasless transactions and social recovery options that feel more like traditional apps.
Environmental Concerns Addressed
Ethereum's transition to proof-of-stake solved its energy consumption issues, cutting energy use by 99.95%. While public perception sometimes lags behind technical reality, this dramatic reduction addresses environmental concerns and remains important for broader adoption.
How Should Someone Get Started with Ethereum?
Getting started with Ethereum is easier than ever, thanks to improved user interfaces and better educational resources. Here's how to begin your journey safely.
Purchasing and Storing ETH
Centralized Exchanges: Platforms like Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken offer the easiest way to buy ETH with traditional payment methods.
Decentralized Exchanges: More experienced users can trade directly through protocols like Uniswap, though this requires already owning some cryptocurrency.
Wallet Selection: MetaMask provides an excellent introduction to Ethereum for beginners, while hardware wallets like Ledger offer maximum security for larger holdings.
Exploring the Ethereum Ecosystem
Official Resources: The ethereum.org website offers comprehensive information about the platform and its ecosystem.
DeFi Protocols: Start with established platforms like Uniswap for trading or Aave for lending. Always begin with small amounts while you learn.
NFT Marketplaces: OpenSea and similar platforms let you explore digital collectibles and art without committing large amounts.
Staking ETH for Rewards
Direct Staking: Requires 32 ETH and technical knowledge to run your own validator node.
Staking Pools: Services like Lido let smaller holders participate in staking and earn rewards proportional to their contribution.
Exchange Staking: Many centralized exchanges offer staking services, though this involves trusting the exchange with your funds.
Conclusion
Ethereum has proven itself as the leading programmable blockchain platform, successfully powering the growth of decentralized finance, digital assets, and Web3 applications. The network's successful transition to proof-of-stake, continuous technical improvements, and thriving developer ecosystem demonstrate both its current capabilities and future potential.
With its robust smart contract functionality, strong economic security model, and ongoing development, Ethereum continues building the infrastructure that supports blockchain technology adoption across multiple industries. The platform's comprehensive approach to decentralized computing has established it as the foundation for the next generation of internet applications.
Learn More: Visit the official Ethereum website or follow @ethereum on X to stay updated.
* Article last updated Aug 2, 2025*
Recent Ethereum Coverage:
- Trust Wallet Adds Gas Sponsorship on Ethereum to Allow Zero Balance Swaps
- Taiko COO on What Fusaka Really Means for Ethereum
- Inside Ethereum’s Plan for Quantum Secure Cryptography
- Ethereum Recent Updates: A Look at Key Network, Market, & Ecosystem Changes
- Ethereum Foundation Plans to Unite Every L2 With Interop Layer
Sources:
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between Ethereum and Bitcoin?
Bitcoin functions as digital currency and store of value, while Ethereum serves as a programmable platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications. Ethereum enables complex applications like DeFi and NFTs.
How much does it cost to use Ethereum?
Main chain transactions cost $1-50 depending on network congestion. Layer-2 solutions like Optimism and Arbitrum offer transactions under $1.
Is Ethereum secure after switching to proof-of-stake?
Yes. Over 1.05 million validators stake ETH to secure the network (as of August 2025). Attacking Ethereum would require controlling 51% of staked ETH, worth hundreds of billions of dollars.
Can I stake ETH with less than 32 ETH?
Yes. Staking pools like Lido allow any amount of ETH to be staked for proportional rewards. Many exchanges also offer staking services.
What happens if Ethereum has technical problems?
Ethereum's decentralized design prevents single points of failure. Thousands of validators and multiple software implementations provide network redundancy.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens
Latest Crypto News
Get up to date with the latest crypto news stories and events


















