Flash Loans Explained: How Crypto's Instant Loans Work

Flash loans let you borrow millions in crypto without collateral. Learn how they work, major platforms, legitimate uses, and why they cause billions in losses.
Crypto Rich
February 24, 2021
Table of Contents
Last revision: November 3, 2025
Flash loans are uncollateralized loans in decentralized finance that must be borrowed and repaid within a single blockchain transaction. The entire process typically takes 12 to 16 seconds. If the borrower cannot repay the loan plus fees before the transaction completes, everything is automatically reversed, making it impossible to default.
This DeFi innovation emerged in 2018 when Marble Protocol first introduced the concept. Since then, flash loans have grown into a significant financial tool. However, this power has attracted both legitimate traders and malicious actors. By mid-2025, crypto hacks and scams had reached over $2.17 billion across 344 incidents, with flash loan attacks accounting for a significant share of these losses.
What Makes Flash Loans Different From Traditional Loans?
Flash loans work nothing like bank loans. While traditional finance requires collateral, credit checks, and lengthy approval processes, flash loans skip all of these requirements.
The core difference lies in atomic execution. An atomic transaction means that every step either completes successfully or fails completely within a single blockchain block.
Here's how the process unfolds:
- A smart contract requests funds from a liquidity pool
- The protocol transfers the requested amount to the borrower's contract
- The borrower executes their intended operations (trading, arbitrage, or other strategies)
- The smart contract attempts to repay the loan plus fees
- If insufficient funds exist for repayment, the blockchain reverses everything
This atomic nature eliminates default risk entirely. The borrowed funds simply return to the pool as if nothing happened.
Flash loans work across multiple blockchain networks. Ethereum remains the largest market, but you'll also find them on BNB Chain, Polygon, Avalanche, Arbitrum, and Fantom. Each chain offers the same basic mechanics with variations in fees and execution speed.
Which Platforms Offer Flash Loans?
Several major DeFi protocols provide flash loan services. Each platform has different features, supported assets, and fee structures. The following platforms lead the flash loan market in 2025.
Aave
With over $41 billion in total value locked as of mid-2025 (equivalent to the 54th largest U.S. bank by deposits), Aave dominates the flash loan market. Operating on Ethereum, Polygon, Avalanche, and other networks, the protocol charges just 0.09% on flash loans, among the lowest fees in DeFi.
The platform offers two flash loan functions. The flashLoan() function allows borrowing from multiple asset pools simultaneously, while flashLoanSimple() borrows from a single reserve pool.
Uniswap and PancakeSwap
Uniswap pioneered flash swaps, which function similarly to flash loans. Instead of borrowing from a lending pool, users borrow from liquidity pools. The V2 protocol introduced this feature, and V4 enhanced it with better routing and lower fees.
PancakeSwap, built on BNB Chain, offers flash swaps through its liquidity pools. The platform charges a 0.3% fee on trades. Many early BNB Chain flash loan attacks used PancakeSwap's pools, including the $45 million PancakeBunny exploit in May 2021.
dYdX
dYdX combines margin trading, lending, and flash loans into a single protocol. The platform offers up to 20x leverage on trades and maintains high liquidity pools. dYdX primarily serves advanced traders who need substantial capital for sophisticated strategies.
Balancer and Equalizer Finance
Balancer allows custom liquidity pools optimized for specific trading strategies. Equalizer Finance expanded flash loan support across multiple chains, including Ethereum, BNB Chain, Optimism, and Polygon, with zero fees.
How Do Traders Use Flash Loans?
Flash loans enable several legitimate trading strategies. Professional traders and DeFi protocols use them to improve capital efficiency and manage risk. These are the most common applications.
Arbitrage Trading
Arbitrage remains the most common use of flash loans. Traders exploit price differences between exchanges by borrowing large amounts, buying low on one platform, and selling high on another.
Example: Token ABC trades at $100 on Exchange A and $102 on Exchange B. A trader borrows $1 million through a flash loan and buys 10,000 tokens on Exchange A. They immediately sell on Exchange B for $1,020,000, repay the $1 million loan plus $900 in fees (0.09%), and pocket $19,100 profit.
The entire process happens in seconds. No upfront capital required. In 2024, Ethereum arbitrage bots executed over $400 million in flash loan trades.
Collateral Swapping
Users with loans on DeFi platforms can swap collateral types without repaying their debt. Here's how: a flash loan pays off the original loan and frees the collateral. The user swaps it for a different asset, deposits the new collateral, and takes out a new loan to repay the flash loan.
This process helps users avoid liquidation when their collateral value drops. It also lets them switch to assets with better returns or lower volatility.
Liquidation Operations
DeFi lending protocols allow third parties to liquidate undercollateralized positions. When a borrower's collateral falls below required thresholds, liquidators can purchase it at a discount.
Flash loans provide the capital to execute large liquidations. Liquidators borrow funds, purchase discounted collateral, sell it at market price, repay the flash loan, and keep the difference. This maintains protocol solvency while providing profit opportunities.
Yield Optimization
Advanced users employ flash loans to maximize yield farming returns. By temporarily increasing position sizes through leverage, they can claim larger rewards from liquidity mining programs. The strategy requires precise timing and gas cost calculations.
What Are Flash Loan Attacks?
Flash loans became infamous for enabling sophisticated attacks on DeFi protocols. These exploits have caused losses of hundreds of millions of dollars since 2020. Understanding how these attacks work helps explain the security challenges facing DeFi.
How Attacks Work
Attackers combine flash loans with smart contract vulnerabilities to drain protocol funds. Most attacks follow the same playbook: borrow massive amounts, manipulate protocol functions, extract value, repay the loan, and walk away with stolen funds.
Common attack vectors include:
- Oracle manipulation by artificially moving token prices
- Liquidity pool draining through AMM exploit
- Reentrancy attacks on vulnerable contracts
- Governance manipulation with temporary voting power
The atomic nature that protects lenders also enables attackers to test exploits risk-free, losing only gas fees when attempts fail.
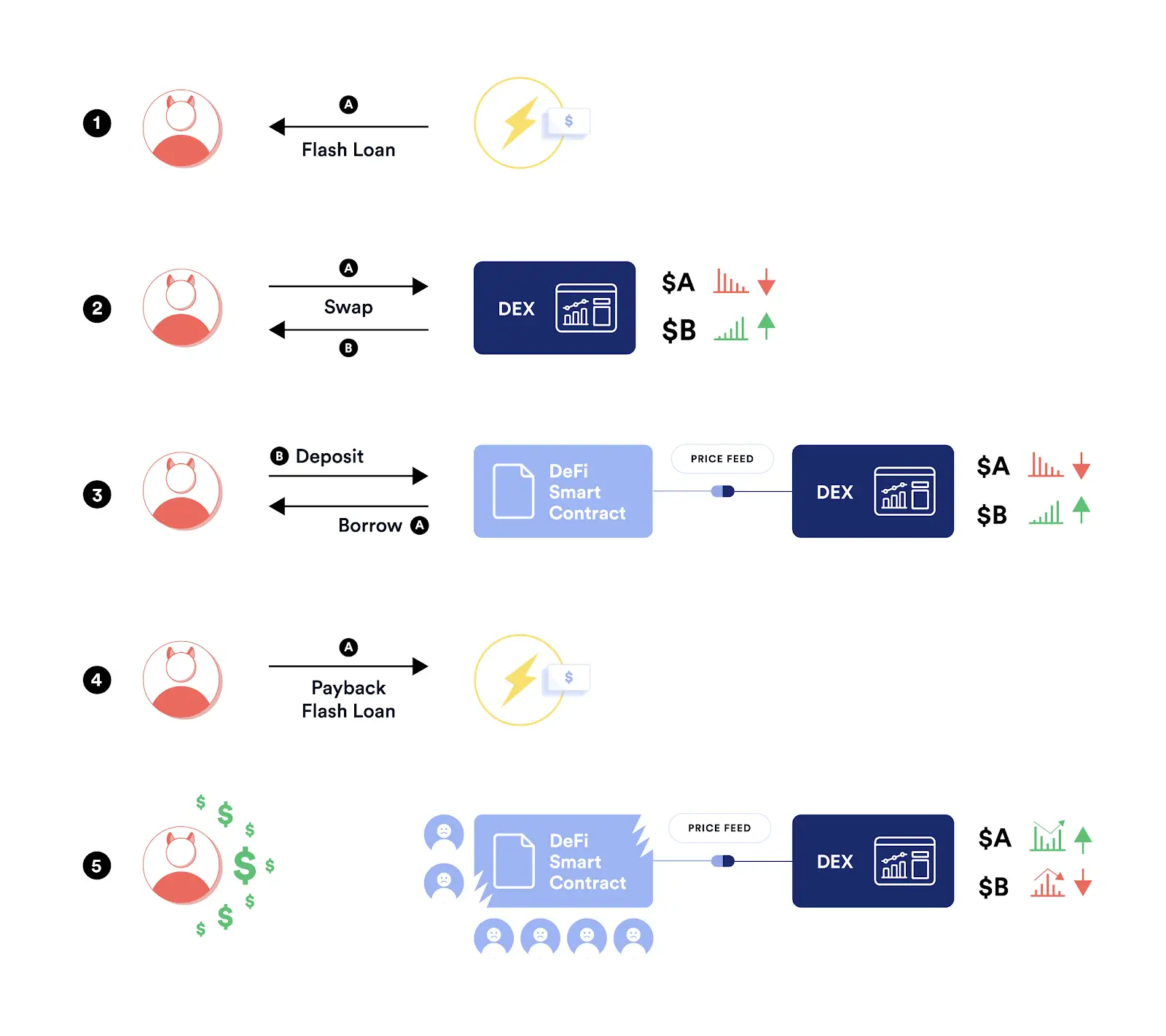
Major Flash Loan Exploits
Several high-profile attacks demonstrate the risks:
Alpha Homora (February 2021): A complex attack using a fake smart contract manipulated Iron Bank lending records, inflating borrowing limits and draining $37 million.
PancakeBunny (May 2021): The BNB Chain protocol lost $45 million in a sophisticated attack. Attackers borrowed BNB and manipulated BUNNY token prices through PancakeSwap pools, minting 6.9 million BUNNY tokens. They dumped these tokens, crashing the price from $146 to $6.17, then repaid the loan.
Cream Finance (October 2021): Exploiters targeted Iron Bank and Alpha Homora connections to steal $130 million through multiple flash loan transactions.
Beanstalk (April 2022): Attackers used flash loans to acquire governance voting power. They borrowed assets, voted to approve a malicious proposal that transferred $182 million to their wallet, executed the proposal, repaid the flash loan, and kept $80 million in profit.
Euler Finance (March 2023): The largest flash loan attack in history stole $197 million. The attacker exploited a vulnerability in the DonateToReserve function to manipulate token balances. They borrowed $30 million DAI from Aave, drained Euler's pools, and transferred funds through Tornado Cash. The attacker later returned the funds and apologized.
2024-2025 Attack Trends
The pace of flash loan attacks accelerated dramatically in 2024 and 2025. Flash loan attacks accounted for 83.3% of recorded exploits in 2024, underscoring their prevalence as an attack vector. By mid-2025, total crypto losses from hacks and scams had exceeded $2.17 billion across 344 incidents.
The surge continued through 2025. April alone saw $92 million stolen across 15 incidents, marking a 124% increase from March. In September 2025, $127 million in exploits was recorded. The KiloEx platform lost $7.5 million in April 2025 through price manipulation attacks.
Recent patterns show attackers targeting newly launched protocols before security audits are complete.
What Risks Come With Flash Loans?
Flash loans carry significant risks for both legitimate users and protocols. Anyone considering flash loan strategies should understand these challenges before attempting transactions.
Technical Complexity
Executing flash loans requires expertise in smart contract development. Users must write contracts that handle borrowing, executing operations, and repaying in a single transaction. Coding errors result in failed transactions and wasted gas fees.
Gas costs on Ethereum can reach hundreds of dollars during network congestion. A failed flash loan wastes these fees with no profit. Competition from MEV bots means slower transactions rarely succeed.
Price Slippage
Large trades move market prices. Flash loan arbitrage opportunities disappear within seconds as prices adjust. What looks profitable at the transaction start may become unprofitable by the time it is executed.
In 2023, a bot executed a sophisticated strategy using a $200 million flash loan, netting only $3.24 in profit. The bot was configured to accept any positive result, even minimal gains after gas costs.
Smart Contract Vulnerabilities
Protocols with unaudited contracts become prime targets. Flash loans don't create vulnerabilities. They amplify them by providing attackers with unlimited capital to exploit weaknesses.
Common vulnerabilities include:
- Unprotected price oracles.
- Reentrancy attack vectors.
- Integer overflow errors.
- Improper access controls.
- Missing validation checks.
Regulatory Uncertainty
Flash loan regulations remain unclear in most jurisdictions. Using flash loans for attacks clearly violates laws. Legitimate arbitrage exists in a gray area.
The United States advanced regulatory frameworks in 2024-2025. The CLARITY Act grants the CFTC jurisdiction over digital commodities while creating DeFi exemptions for code development and node operations.
How Can Protocols Prevent Flash Loan Attacks?
DeFi platforms implement multiple security measures to protect against flash loan exploits. These defense strategies reduce attack surfaces and protect user funds.
Decentralized Oracles
Price oracle manipulation causes many flash loan attacks. Protocols increasingly use decentralized oracle networks like Chainlink to aggregate data from multiple sources. Single-source oracles become vulnerable to manipulation.
Time-weighted average price (TWAP) oracles reduce manipulation risk by averaging prices across multiple blocks rather than relying on spot prices.
Smart Contract Audits
Regular security audits identify vulnerabilities before attackers find them. Top audit firms like CertiK, Hacken, and OpenZeppelin review contract code for common exploits.
Bug bounty programs incentivize white hat hackers to report vulnerabilities privately. Major protocols offer rewards ranging from $10,000 to $1 million for critical discoveries.
Transaction Monitoring
Real-time monitoring systems detect suspicious activities. Large flash loan transactions trigger alerts for security teams to investigate. Some protocols implement automatic pauses when unusual patterns emerge.
Rate Limiting
Limiting transaction sizes and frequencies reduces the impact of attacks. Protocols may cap flash loan amounts or require time delays between large transactions.
Multi-Signature Controls
Critical protocol functions require multiple signatures from different parties. This prevents single attackers from exploiting governance or upgrade mechanisms through flash loan voting power.
Are Flash Loans Legal?
Flash loans themselves are legal financial tools. Legitimate uses such as arbitrage, collateral swapping, and liquidations promote market efficiency and protocol stability across most jurisdictions.
Using flash loans for attacks violates multiple laws. Theft, fraud, computer crimes, and securities violations all apply to malicious flash loan activities. Several attackers faced criminal charges and extradition requests.
Users should consult legal counsel before engaging in flash loan strategies. Laws vary significantly between jurisdictions.
Where Is Flash Loan Technology Heading?
Cross-chain functionality now allows borrowing on one blockchain and repaying on another through bridge protocols and atomic swaps, unlocking deeper liquidity pools. Meanwhile, MEV (Maximum Extractable Value) bots have taken over. These algorithms consume 40% of Solana's blockspace and execute thousands of daily transactions with institutional-grade infrastructure that leaves individual traders at a disadvantage.
Privacy solutions like Flashbots Protect now shield transactions from front-running, while AI and machine learning algorithms detect multi-step arbitrage paths invisible to human traders. Real-world asset integration is bridging DeFi with traditional finance through tokenized real estate, invoices, and commodities.
Security continues to improve as protocols implement better oracle designs, formal verification methods, and automated monitoring. As these defenses mature and regulations clarify, flash loans will remain a fundamental DeFi primitive: expanding legitimate use cases while narrowing attack vectors.
Sources
- Bank of Canada. (2025). "Risk-Free Uncollateralized Lending in Decentralized Markets: An Introduction to Flash Loans." Staff Discussion Paper 2025-6.
- FraudNet. (2025). "Flash Loan Attacks Definition."
- ImmuneBytes. (2024). "List of Flash Loan Attacks in Crypto."
- DeFi Overview. (2025). "Top 10 Best DeFi Lending Platforms in 2025."
- Amber Group. (2021). "BSC Flash Loan Attack: PancakeBunny."
- OWASP. (2025). "SC07:2025 - Flash Loan Attacks."
- Chainalysis. (2024). "2024 Crypto Crime Report."
- Halborn. (2024). "Flash Loan Attack Statistics and Trends."
- Immunefi. (2025). "Monthly DeFi Exploit Reports."
- DeepStrike. (2025). "2025 Crypto Security Analysis."
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does a flash loan cost?
Flash loan fees typically range from 0.05% to 0.3% of the borrowed amount. Users also pay blockchain gas fees, which vary based on network congestion and can reach hundreds of dollars during peak times.
Can anyone take out a flash loan?
Technically yes, but flash loans require smart contract programming knowledge. Users must write custom contracts that handle borrowing, executing operations, and repaying within one transaction. Pre-built templates and tools like DeFiSaver lower barriers for non-programmers.
What happens if I cannot repay a flash loan?
The entire transaction automatically reverses if repayment fails. Borrowers lose only the gas fees paid for the failed transaction.
Why do protocols offer flash loans?
Protocols earn fees on every flash loan transaction. These fees generate revenue for liquidity providers. Flash loans also increase trading volume and capital efficiency across DeFi ecosystems, benefiting the entire protocol by attracting users and liquidity.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens





















