What is Polkadot (DOT)? Complete Guide to the Multi-Chain Protocol

Complete guide to Polkadot blockchain protocol - architecture, tokenomics, governance, and ecosystem. Learn how DOT powers Web3 interoperability and parachain technology.
Crypto Rich
May 26, 2025
Table of Contents
Polkadot operates as a layer-0 protocol that enables interoperability, scalability, and shared security for independent blockchains called parachains. Founded by Dr. Gavin Wood, Ethereum's co-founder, Polkadot launched its mainnet on May 26, 2020, transitioning from Proof-of-Authority to Nominated Proof-of-Stake by June 2020, with governance fully decentralized by July 2020.
The protocol addresses three fundamental challenges in blockchain technology: scalability, interoperability, and governance. Through its unique architecture, Polkadot can process high transaction volumes via parallelized parachains while maintaining unified security. Recent performance tests demonstrate the network's capability to handle at least 623,000 transactions per second, positioning it as a leading infrastructure for Web3 applications.
How Polkadot's Multi-Chain Architecture Works
The Relay Chain Foundation
The Relay Chain serves as Polkadot's core infrastructure, handling consensus, security, and interoperability through Nominated Proof-of-Stake. Like air traffic control coordinating multiple airports, the Relay Chain manages communication and security across all connected parachains. The system uses the Phragmén election method to select validators who secure the network and process essential transactions, including governance proposals, staking operations, and parachain bonding.
The Polkadot Host provides the environment that interacts with the runtime - a WebAssembly blob that handles state transitions. This modular design includes networking through Libp2p, state storage, consensus engines (BABE and GRANDPA), and cryptographic primitives using Blake2b hashing and Sr25519 signatures. The architecture allows alternative Host implementations while treating the runtime as a black box, enhancing flexibility for developers.
Parachains: Sovereign Chains with Shared Security
Parachains function as independent layer-1 blockchains tailored for specific use cases, from decentralized finance to gaming applications. Think of parachains as specialized lanes on a superhighway - each lane serves different types of traffic but all benefit from the same road infrastructure and security systems. Each parachain connects to the Relay Chain to benefit from shared security while maintaining sovereignty over its operations.
The parallel processing capability enables remarkable performance. A 2024 benchmark test called "The Spammening" demonstrated Polkadot's theoretical capacity to handle at least 623,000 transactions per second at just 23% network core utilization on Kusama, with results scalable to the main Polkadot network. While real-world performance varies based on parachain activity and network conditions, this benchmark underscores the protocol's potential to simultaneously process high transaction volumes across multiple parachains.
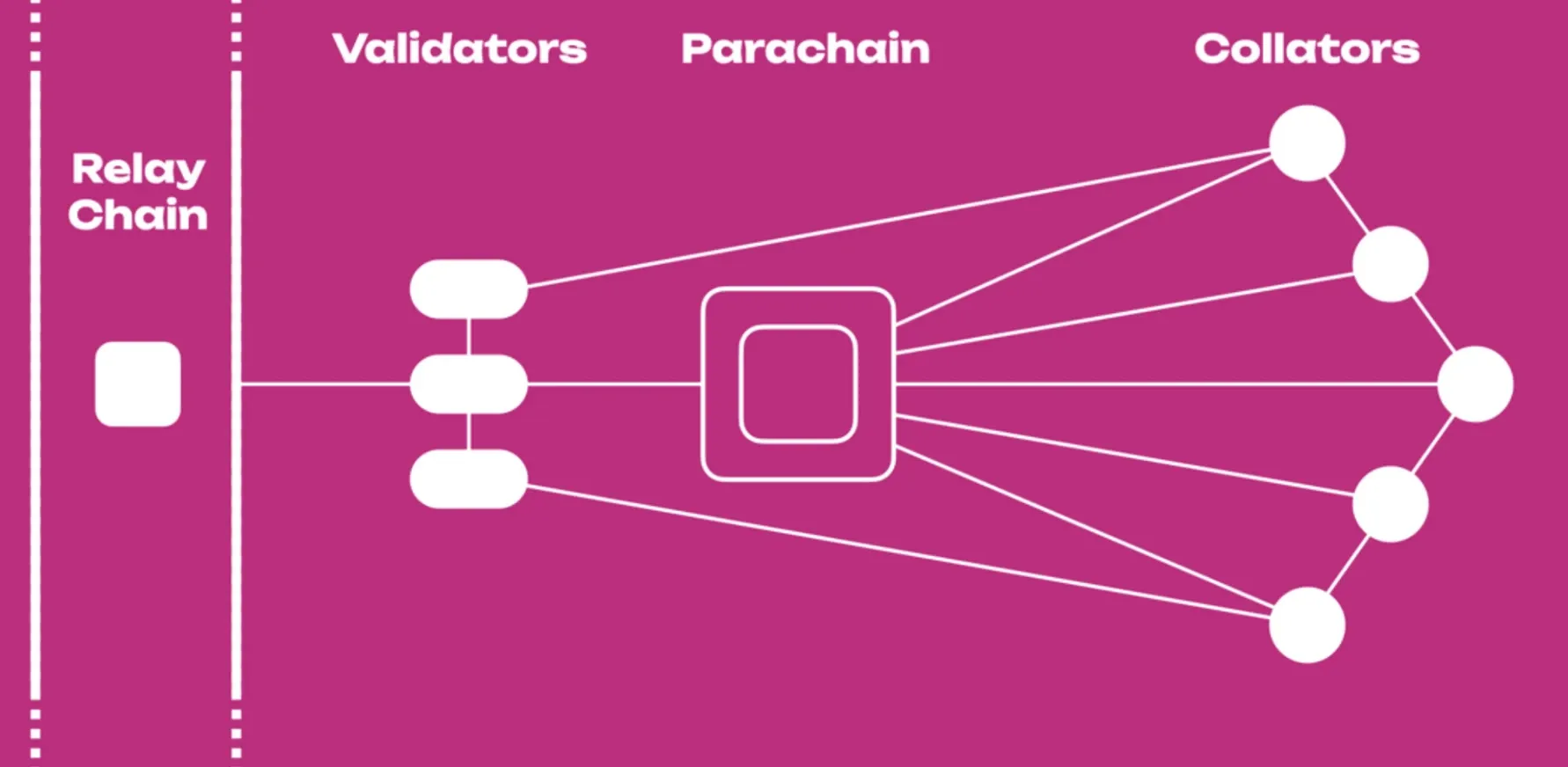
Parathreads and Bridge Connections
Parathreads offer a pay-as-you-go alternative to full parachain slots, allowing smaller projects to access Polkadot's security without securing dedicated positions. This system reduces costs for lighter applications while maintaining access to the network's protection mechanisms.
Bridges enable connections to external networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin using Polkadot's Cross-Consensus Messaging (XCM) format. XCM v3, launched in June 2023, supports NFT transfers and advanced programmability. By May 2025, it had facilitated $125 million in monthly cross-chain transfers, demonstrating the effectiveness of trustless cross-chain communication.
Consensus Mechanisms: BABE and GRANDPA
Polkadot's hybrid consensus combines BABE (Blind Assignment for Blockchain Extension) for block production with GRANDPA (GHOST-based Recursive Ancestor Deriving Prefix Agreement) for deterministic finality. BABE uses Verifiable Random Functions (VRF) for fair validator assignment, avoiding computational intensity issues found in other randomness systems.
This combination ensures fast, secure transactions with current block times of 6 seconds, potentially reducing to 2-3 seconds post-optimization. The system maintains consistent performance while providing the deterministic finality crucial for cross-chain operations.
DOT Token Economics and Network Incentives
Primary Functions of DOT
The DOT token, with its smallest unit being the Planck (1 DOT = 10^10 Planck following the 2020 redenomination), serves multiple essential functions:
- Governance: DOT holders participate in OpenGov referenda across 15 governance tracks, with conviction voting that amplifies influence through longer token locks
- Network Security: Staking through Nominated Proof-of-Stake rewards validators and nominators for securing the Relay Chain and parachains
- Parachain Operations: Projects lock DOT for 6-24 month leases or purchase Coretime (computational resources) for flexible parachain resource allocation
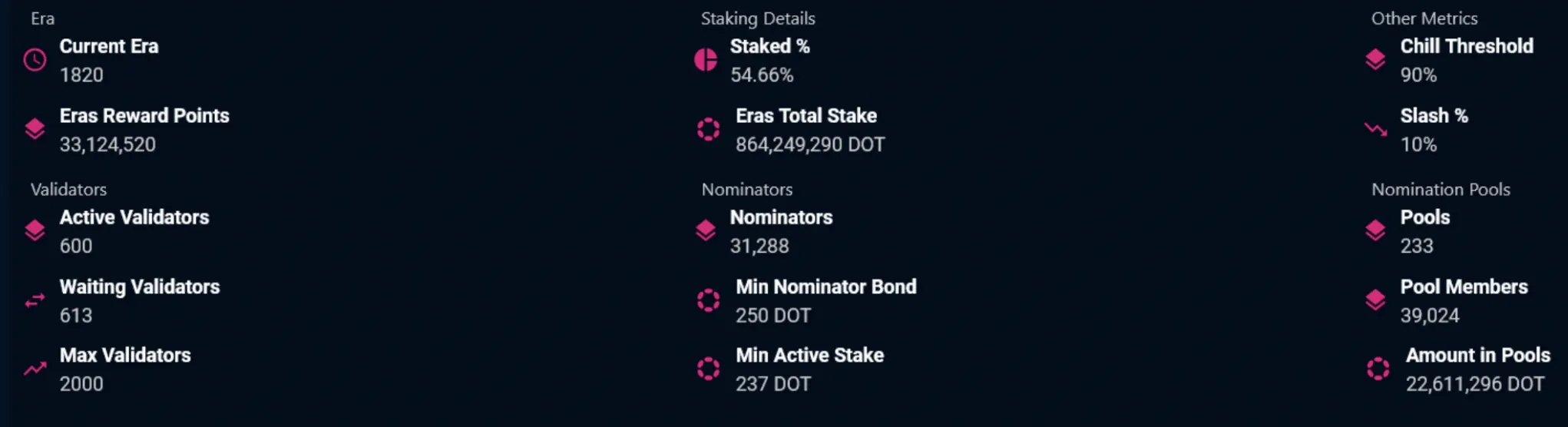
Supply Dynamics and Inflation Model
Polkadot operates with an uncapped token supply that targets a 50% staking rate across the network. The system uses dynamic inflation adjustments up to 10% annually to maintain this target participation level. The initial supply of 1 billion DOT was established after the 100x redenomination in August 2020, with the current circulating supply having grown to approximately 1.58 billion DOT through ongoing inflation.
The redenomination occurred at block #1,248,328 and made token amounts more user-friendly while preserving all economic relationships. Beyond traditional uses, DOT now serves to purchase computational resources for parachains and reserve parachain identifiers for rollups, expanding its role in ecosystem scalability.
Treasury Funding and Distribution
Network inflation directs a portion of newly minted DOT to the Treasury, which funds ecosystem development through grants and bounties. The Web3 Foundation Grants Program exemplifies this approach, supporting over 500 projects across 50 countries. All Treasury spending decisions go through OpenGov referenda, ensuring transparent, community-driven resource allocation.
Parachain auctions and the new Agile Coretime system temporarily reduce circulating supply as projects lock DOT for operational periods. This mechanism creates natural economic cycles that balance ecosystem growth incentives with token scarcity dynamics.
OpenGov: Decentralized Protocol Governance
Evolution from Governance V1
OpenGov launched in June 2023 as a complete replacement for Polkadot's original governance system. It removes centralized entities like councils and technical committees. The new system empowers DOT holders with direct control over all network decisions through 15 specialized governance tracks.
Each track handles specific types of proposals with tailored parameters. For example, the Root track for high-impact changes requires 48.2% support on day one, dropping to near 0% by day 28. The multi-role delegation system allows DOT holders to assign voting power to experts for specific tracks, enhancing participation without requiring deep technical knowledge from every token holder.
Community-Driven Decision Making
The referenda process requires both Submission Deposits and Decision Deposits for proposals to progress through the Decision Period. Approval and support criteria vary by track, with the Wish For Change track enabling non-binding consensus signaling for community sentiment without impacting network state.
This transparent, on-chain governance ensures all proposals and voting results remain publicly accessible. Recent community decisions include approving technical upgrades like Asynchronous Backing and funding security tools like SCOUT, demonstrating the system's effectiveness in driving protocol evolution.
Expanding Ecosystem and Real-World Applications
Major Parachain Applications
Polkadot's ecosystem encompasses over 300 projects spanning diverse use cases:
- Acala: Operates as Polkadot's primary DeFi hub, enabling cross-chain liquidity and decentralized applications while demonstrating specialized parachain functionality
- Moonbeam: Provides Ethereum EVM compatibility within Polkadot's environment, allowing teams to deploy existing Ethereum applications as parachains
- Phala: Focuses on privacy-preserving cloud computing solutions for enterprise and consumer applications
- Bitfrost: Offers DeFi protocols with staking rewards and liquidity options across multiple networks
- Mubert: Represents innovation in decentralized AI music platforms, showcasing Polkadot's versatility beyond traditional blockchain applications
Technical Activity and Growth Metrics
The Polkadot SDK, built on the Substrate framework, enables rapid development of custom blockchains using Rust programming and the ink! smart contract language. Substrate's modular design includes pre-built modules for governance, consensus, and other common blockchain functions, with smart contracts compiled to WebAssembly for efficient execution.
Kusama serves as Polkadot's experimental "canary" network, sharing nearly identical code while hosting live testing of new features before mainnet deployment. This approach reduces risks for production applications while enabling continuous innovation.
The ecosystem benefits from comprehensive tooling including block explorers like Subscan.io and Polkascan for real-time chain data, plus the Polkadot-JS UI for interactive governance tracking and network interaction.
Web3 Foundation Support Programs
The foundation provides comprehensive ecosystem support through multiple channels:
- Grants Program: Has funded over 500 initiatives covering infrastructure, applications, and research advancing Web3 adoption globally
- Polkadot Assurance Legion (PAL): Reimburses audit costs for network projects, ensuring high security standards across applications
- Educational Platforms: DotCodeSchool and the Blockchain Fundamentals MOOC provide free, accessible learning covering cryptography, networks, and Web3 concepts
- Community Tools: GitHub contribution guidelines and development resources enhance transparency and lower barriers for new contributors
Recent Technical Advances and Future Development
Performance and Accessibility Improvements
Recent upgrades significantly enhance network capabilities:
- Asynchronous Backing: Implemented in 2024, this upgrade reduces block times across parachains, with some like Hydration achieving 6-second blocks, improving DeFi performance and user experience
- XCM v3 Evolution: Enhanced cross-chain messaging supports $125 million in monthly transfers, with advanced programmability and NFT transfer capabilities
- Agile Coretime: Simplifies parachain deployment by enabling on-demand computational resource purchases rather than requiring long-term slot commitments
- Smart Contract Integration: The May 2025 OpenZeppelin partnership introduces Ethereum-compatible smart contract libraries and development tools, reducing migration barriers for existing projects
Next-Generation Architecture
The JAM (Join-Accumulate Machine) protocol, detailed in the Grey Paper, represents ongoing research into enhanced scalability frameworks. JAM focuses on secure and efficient computation to support future network growth while maintaining Polkadot's security guarantees.
Development continues on this next-generation architecture, which aims to further improve transaction processing capabilities and parachain diversity support.
Technical Infrastructure and Developer Support
Substrate Framework Capabilities
Substrate's modular framework enables teams to create custom blockchains with configurable governance, consensus, and functionality modules. The Rust-based programming environment provides memory safety and performance optimization, while the ink! smart contract language compiles to WebAssembly for efficient cross-parachain execution.
The framework's flexibility allows developers to select specific modules based on project requirements, significantly reducing development time compared to building blockchains from scratch.
Security and Cryptographic Foundation
Polkadot employs robust cryptographic mechanisms to ensure network security:
- Sr25519 Signatures: Uses Schnorr signatures over Curve25519 for efficient key derivation and signing with native multisignature support
- Verifiable Random Functions: VRF ensures fair validator assignment for BABE consensus, providing consistent block times
- Future Enhancements: GRANDPA plans to adopt BLS keys for signature aggregation, further improving efficiency
Native Account Abstraction: Unlike Ethereum's ERC-4337 approach that requires smart contracts, Polkadot has account abstraction built into its core architecture through Substrate's FRAME system. This enables flexible origin abstraction where functions can be called by any origin (not just accounts), including governance origins, proxy accounts, and multisig arrangements. Users can implement social recovery, role-based proxy accounts, transaction batching, and gasless transactions natively without needing separate smart contract layers.
Advanced Account Features: The system supports multisignature accounts, derivative accounts from the same parent key, pure proxy accounts for enhanced privacy, and cross-chain account interactions through XCM. This native flexibility allows developers to create sophisticated account management systems without the complexity and gas costs associated with smart contract-based solutions.
Security tools like SCOUT, developed by Coinfabrik with Polkadot DAO funding, enhance code security by identifying vulnerabilities and providing secure development recommendations.
Data Availability and Decentralization
The network ensures data availability for full nodes to verify transactions while maintaining historical data retrievability for syncing and queries. The Polkawatch app tracks node distribution to prevent centralization risks from single providers or geographic regions, supporting Polkadot's high decentralization standards.
Market Position and Industry Recognition
Institutional Adoption
A 2025 Nasdaq request to list a Grayscale ETF holding DOT demonstrates growing institutional confidence in Polkadot's interoperable architecture. This development recognizes the protocol's potential to serve as foundational Web3 infrastructure.
The emphasis on true interoperability rather than simple bridging solutions distinguishes Polkadot from single-chain networks. It supports diverse use cases while maintaining unified security guarantees.
Competitive Advantages
Polkadot's shared security model provides smaller projects access to enterprise-grade protection without individual network maintenance costs. The protocol's focus on sovereignty allows parachains to maintain independent governance while benefiting from network effects and cross-chain communication capabilities.
Unlike other multi-chain solutions, Polkadot offers distinct advantages: Ethereum 2.0's sharding shares computational load but lacks true chain sovereignty, Cosmos requires each chain to secure itself independently, and Avalanche's subnets don't share security by default. Polkadot combines the benefits of shared security with complete parachain independence, creating unique value propositions for teams requiring both customization and connectivity in their blockchain applications.
Community Resources and Getting Started
Documentation and Learning Materials
The Polkadot Wiki is a comprehensive resource hub, offering guides like "Polkadot for Beginners" alongside detailed technical specifications. Community-driven content ensures documentation stays current with protocol updates and new feature releases.
Interactive tools include the Polkadot-JS UI for governance tracking and network interaction, plus Algolia search functionality and React components for live on-chain data integration.
Development Support and Funding
Multiple support channels assist developers and projects:
- Technical Resources: GitHub contribution guidelines, development forums, and community feedback channels
- Educational Programs: DotCodeSchool teaches practical Substrate development while the Blockchain Fundamentals MOOC covers theoretical foundations
- Financial Support: Grants, bounties, and audit cost reimbursement through PAL help projects launch and maintain security standards
The combination of technical tools, educational resources, and financial support creates a comprehensive ecosystem for blockchain innovation.
Conclusion
Polkadot has established itself as Web3's foundational layer-0 infrastructure through its multi-chain architecture, community-driven governance, and developer-friendly ecosystem. With demonstrated capacity for 623,000 transactions per second, advanced cross-chain messaging through XCM v3, and simplified deployment via Agile Coretime, the protocol drives scalable, interoperable blockchain innovation.
Polkadot's technical design makes it ideal for applications that need both independence and connection to other chains. The OpenGov system lets the community guide how the protocol develops, keeping control decentralized rather than in the hands of a few developers.
The network continues attracting new projects, developers, and institutional investors because it solves a real problem: how to connect different blockchains without forcing them to give up control. With strong technical foundations, extensive support programs, and transparent decision-making, Polkadot provides the infrastructure needed for a truly connected decentralized web.
Visit the official Polkadot website to learn more about the ecosystem, access developer resources, and discover parachain projects. Follow @Polkadot on X for the latest updates, technical developments, and community news.
Read Next...
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens