RISE Chain: The Fastest Ethereum Layer 2

RISE Chain delivers unmatched speed with 5ms latency and 100,000+ TPS while maintaining Ethereum compatibility and decentralization. Learn how this next-generation Layer 2 solution is revolutionizing blockchain performance.
Crypto Rich
May 20, 2025
Table of Contents
Why Today's Ethereum Scaling Solutions Fall Short
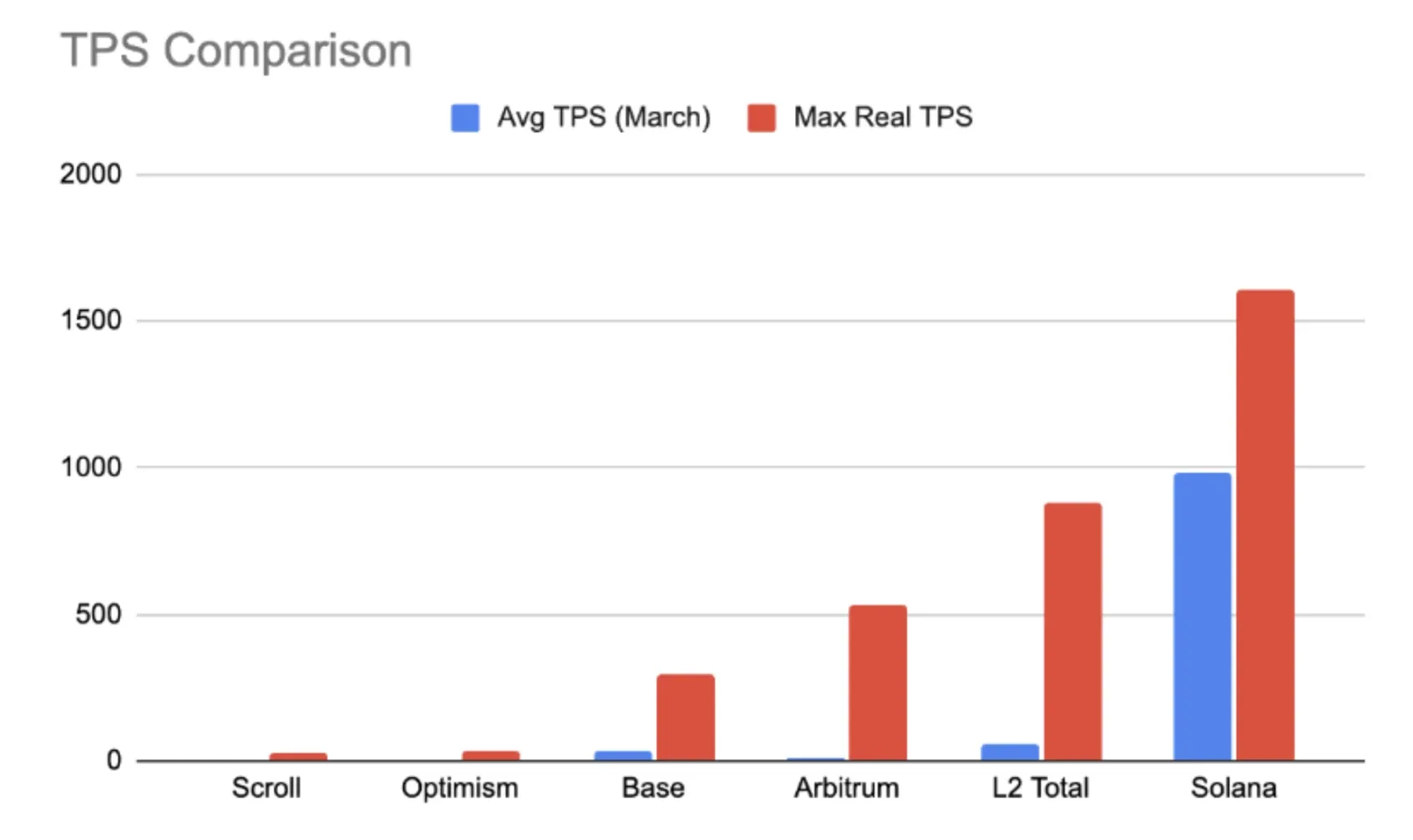
The blockchain world faces a critical challenge: Ethereum's Layer 2 (L2) networks collectively process only about 100 transactions per second (TPS), despite holding over $40 billion in value. This limitation creates bottlenecks during peak usage, causing transaction delays and high fees that frustrate users and developers alike.
Layer 1 alternatives like Solana deliver approximately 1,000 TPS but sacrifice decentralization to achieve this performance. Meanwhile, existing L2 solutions such as Arbitrum and Base have hit ceilings of 532 TPS and 293 TPS respectively, often experiencing outages when traffic surges.
Ethereum's roadmap includes "The Surge," which targets 100,000 TPS capability. Yet the performance gap between current offerings and this ambitious goal reveals the market's need for faster Ethereum-compatible solutions that maintain decentralization and security fundamentals.
What Makes RISE Chain Different
Addressing these performance limitations head-on, RISE Chain enters the market as an Ethereum Layer 2 blockchain built on the Rust-based Reth SDK. According to official claims, RISE delivers transaction confirmations with just 5 milliseconds (ms) of latency, positioning it as the blockchain industry's speed leader.
The protocol targets more than 100,000 TPS and 1 Gigagas per second processing power while maintaining full EVM compatibility. This approach allows developers to deploy existing Ethereum smart contracts without modifications, eliminating technical barriers to adoption.
Evidence of RISE's capabilities already exists in its testnet performance. On May 8, 2025, @rise_chain reported on X that the testnet processed 1 billion transactions, including 50,000 transactions in a single 1-second block – metrics that far exceed today's operational L2 networks.
The project has attracted significant financial backing, raising $3.2 million from prominent investors including Ethereum co-founder Vitalik Buterin, Polygon co-founder Sandeep Nailwal, Finality Capital Partners, MH Ventures, and others. This capital infusion, announced on Sept 16, 2024, has helped fund the testnet's development and ongoing airdrop farming program.
Where other high-performance blockchains diverge from Ethereum's principles, RISE maintains alignment with its core values, functioning as an extension of the ecosystem rather than a competing alternative.
The Technology Behind RISE Chain's Performance
The extraordinary speed of RISE Chain stems from several technical breakthroughs working in concert. These innovations transform traditional blockchain bottlenecks into pathways for parallel processing and efficient state management.
Parallel EVM: 22x Faster Execution
At the heart of RISE's performance advantage lies its parallel Ethereum Virtual Machine (pEVM). Unlike traditional EVMs that process transactions one-by-one, like a single-lane road, RISE's pEVM handles multiple transactions simultaneously, like a multi-lane highway.
Tests documented in the whitepaper demonstrate the pEVM achieving peak execution throughput of 55 Gigagas per second on 32 AWS Graviton3 CPUs. This represents a 22x speedup compared to sequential execution methods used by competing blockchains.
The development team chose Rust over Go (which powers systems like Polygon and Sei) to minimize runtime overhead. The pEVM implementation uses Block-STM's optimistic execution approach, allowing parallel transaction processing while maintaining deterministic outcomes – a critical requirement for blockchain consensus.
Developers can examine this technology directly, as the code remains open-source and available at github.com/risechain/pevm, enabling community review and contributions to the codebase.
Continuous Block Pipeline: Near 100% Execution Time
Traditional blockchains suffer from inefficient resource utilization. Block production typically consists of sequential stages that leave execution resources idle for significant periods. RISE changes this paradigm through its Continuous Block Pipeline (CBP).
Like a non-stop assembly line, RISE's CBP parallelizes stages, enabling execution nearly 100% of the time. Sequential pipelines, by contrast, typically utilize execution resources just 8% of the time. This nearly 12-fold improvement in resource utilization allows RISE to process transactions almost continuously, eliminating the waiting periods that plague other networks during high demand.
Optimized State Storage and Access
State access represents another performance constraint in conventional blockchains. RISE addresses this by replacing Ethereum's Merkle-Patricia Trie (MPT) with a Versioned Merkle Tree that significantly reduces storage overhead.
The system also employs a log-structured storage approach inspired by LETUS. This design minimizes the number of read and write operations required for each transaction – operations that traditionally consume substantial resources.
Additional optimizations include lowering the Merkle tree radix to reduce computational complexity, carefully balancing read and write operations for maximum throughput, and implementing multi-version data structures to handle state conflicts without blocking execution.
Advanced Networking and Execution
Network communication often limits blockchain performance. RISE implements the QUIC protocol instead of traditional TCP connections, providing faster connection establishment and lower latency in the sequencer mempool – where transactions wait to be processed.
For smart contract execution, the system supports Just-in-Time (JIT) compilation for native VM execution. This flexibility allows RISE to switch between JIT and interpreter-based execution depending on deployment requirements, optimizing for either speed or compatibility as needed.
Smart Mempool Management
Pending transactions in a blockchain's mempool can lead to execution dependencies that limit parallelism. RISE overcomes this challenge with an intelligent mempool structure that pre-orders transactions to minimize shared states.
Similar to Solana's local fee market, the system dynamically adjusts costs for congested smart contracts. When specific contracts experience heavy usage, their gas costs automatically increase. This market-based approach encourages developers to write efficient code while helping manage network load through economic incentives rather than arbitrary limits.
Maintaining Ethereum's Decentralization Values
Despite its pursuit of performance gains, RISE Chain does not abandon Ethereum's commitment to decentralization. While many high-speed blockchains compromise on this principle, RISE's architecture specifically aims to preserve it.
Based Sequencing: Using Ethereum Validators
Social media posts from @rise_chain on X (May 7 and May 11, 2025) confirm plans to implement based sequencing – a technique that uses Ethereum's validators instead of a centralized sequencer. This approach enhances both interoperability with the Ethereum ecosystem and the decentralization of the RISE network itself.
By leveraging Ethereum's security model while delivering performance improvements, RISE positions itself as complementary to Ethereum rather than competitive. This alignment with Ethereum's long-term vision distinguishes RISE from alternative L1 blockchains that pursue performance at the expense of decentralization.
Optimistic Rollup with Future zkEVM Plans
The RISE team selected an optimistic rollup approach for their initial implementation due to its ability to achieve high throughput without specialized hardware requirements. However, the whitepaper outlines a transition path to a zero-knowledge EVM (zkEVM) once hardware solutions like zkASIC become widely available.
This forward-looking strategy allows RISE to deliver high performance immediately while preparing for even greater security and scalability in the future. The approach demonstrates RISE's commitment to long-term development rather than short-term performance gains.
How RISE Compares to Other Blockchains
The blockchain landscape features several competing approaches to scaling. When comparing RISE to existing solutions, several key differences emerge in both architecture and performance characteristics.
RISE vs. Solana
Solana currently achieves approximately 1,000 TPS but relies on a lower validator count and high token emissions to maintain its network. These design choices limit decentralization in exchange for performance.
RISE targets 100× Solana's throughput while maintaining stronger decentralization through its Ethereum alignment. This approach potentially offers developers and users the best of both worlds: Solana-exceeding performance with Ethereum-level security guarantees.
RISE vs. Current Ethereum L2s
Today's Ethereum L2 solutions demonstrate significantly lower performance ceilings than RISE aims to provide. Arbitrum has reached a maximum of 532 TPS during peak usage, while Base has topped out at 293 TPS.
Both networks have experienced service disruptions during periods of congestion. RISE's architecture, with its parallel execution and optimized state management, specifically addresses these limitations. The system design aims to handle peak loads without the service interruptions that have plagued existing L2 networks during high-demand periods.
Users can already explore the testnet's capabilities at portal.risechain.com, where the team has demonstrated the platform's potential through ongoing airdrop farming initiatives.
Future Directions and Challenges
While RISE presents promising technological advances, the team faces several challenges as they move from testnet to mainnet and beyond.
Future Research Areas
The whitepaper outlines several directions for ongoing development. The team plans to create a composable modular ecosystem, though details remain limited. Further optimization of the parallel EVM performance continues, with the potential to increase throughput even beyond current targets.
Contributions back to the Reth project represent another priority, potentially improving the broader Ethereum ecosystem. The team also continues exploring additional decentralization mechanisms to further strengthen the network's resilience against various attack vectors.
What RISE Chain Means for Blockchain Applications
The performance capabilities offered by RISE could enable entirely new categories of blockchain applications that traditional networks cannot support due to speed limitations.
High-frequency trading platforms could leverage RISE's millisecond settlement times to bring sophisticated trading strategies on-chain. Game developers might build real-time experiences with on-chain transactions for in-game actions, eliminating the lag that has hampered blockchain gaming adoption.
Large-scale social applications could process interactions immediately, creating seamless user experiences similar to centralized alternatives. DeFi protocols requiring complex transaction sequences could execute operations that would time out on slower networks.
These applications have remained limited or impossible on existing blockchains due to fundamental performance constraints. RISE's architecture specifically addresses these limitations, potentially unlocking new use cases that combine decentralization with responsive user experiences.
Conclusion: The Dawn of the Gigagas Era
RISE Chain represents a significant advancement in Ethereum's Layer 2 ecosystem. Its approach delivers previously unattainable performance while remaining faithful to the core principles that make Ethereum valuable to users and developers.
The combination of speed, throughput, and full EVM compatibility positions RISE as a platform merging Ethereum's security and ecosystem advantages with performance exceeding even the fastest Layer 1 alternatives. The testnet's demonstrated capabilities suggest these ambitious performance targets are technically achievable.
As RISE moves toward mainnet launch, it stands as a potential solution to help Ethereum achieve its "Surge" scalability goals. The road ahead contains both technical challenges and implementation hurdles, but the foundation appears solid.
For those wishing to explore further, visit their website at risechain.com/ or follow @rise_chain on X.
Read Next...
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Crypto Rich
Crypto RichRich has been researching cryptocurrency and blockchain technology for eight years and has served as a senior analyst at BSCN since its founding in 2020. He focuses on fundamental analysis of early-stage crypto projects and tokens and has published in-depth research reports on over 200 emerging protocols. Rich also writes about broader technology and scientific trends and maintains active involvement in the crypto community through X/Twitter Spaces, and leading industry events.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens