Internet Computer Faces Major Tokenomics Reset as DFINITY Unveils “Mission 70”

DFINITY releases Mission 70 white paper outlining plans to cut ICP inflation by 70% and scale Internet Computer adoption by 2026.
Soumen Datta
January 15, 2026
Table of Contents
The DFINITY Foundation has released a new white paper titled “Mission 70 and Accelerating the Internet Computer Economy” that lays out a detailed plan to reduce ICP token inflation by at least 70% by the end of 2026 while expanding real-world use of the Internet Computer. Authored by founder Dominic Williams and published on Jan. 13, 2026, the document focuses on concrete changes to tokenomics, infrastructure rewards, and onchain usage rather than broad vision statements.
What Is Mission 70 And Why Does It Matter?
Mission 70 is a structured strategy to rebalance the Internet Computer’s economic model as the network moves beyond its early bootstrapping phase. Since genesis in May 2021, the ecosystem has grown rapidly, but inflation remains high due to generous voting rewards and node provider incentives designed to attract early participation.
DFINITY argues that these parameters now exceed what is required to maintain security and decentralization. Mission 70 responds by proposing specific changes to reduce supply growth while increasing demand through higher network usage.
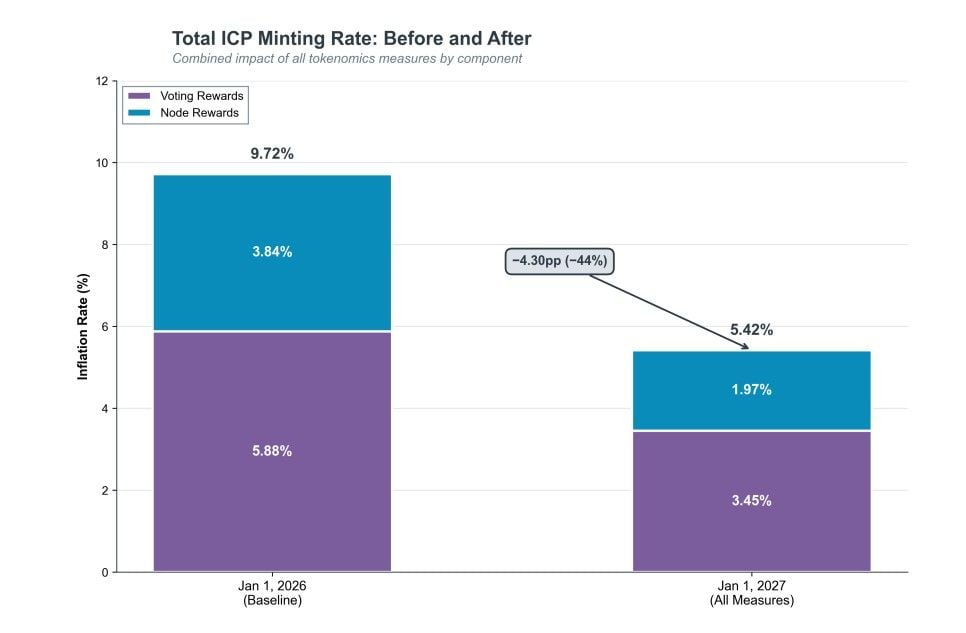
Worth noting, ICP inflation is projected to fall from 9.72% in January 2026 to 2.92% by the end of 2026.
How Does Mission 70 Plan To Reduce Inflation?
The white paper outlines a two-part approach that combines supply-side reductions with demand-side acceleration. Both are required to reach the 70% target.
According to DFINITY’s estimates:
- 44% of the reduction will come from supply-side reforms
- 26% will come from increased ICP burn driven by higher network usage
Together, these measures aim to align inflation with the network’s maturity and actual economic activity.
What Supply-Side Changes Are Being Proposed?
Supply-side reforms focus on reducing the amount of new ICP minted through rewards. The paper argues that current reward levels reflect early-stage incentives rather than ongoing infrastructure costs.
An introductory context is important here. Voting rewards and node provider payments were intentionally high to compensate for long lockup periods and limited early adoption. That phase is ending.
The proposed supply-side changes include:
- Lower voting rewards through shorter dissolve delays
- Replacement of the linear dissolve-delay bonus with a convex curve
- A cap on the total voting reward pool after the initial bootstrapping phase
- A simpler maturity modulation mechanism linked to long-term price deviations
- Reduced rewards for legacy Gen-1 nodes
- Greater reliance on SEV-capable hardware for smaller, more secure subnets
DFINITY estimates these changes will reduce ICP minting from 9.72% in January 2026 to 5.42% by January 2027, a 44% reduction.
How Will Voting Rewards Change Under Mission 70?
Voting rewards are central to Internet Computer governance. ICP holders stake tokens into neurons, which vote on proposals through the Network Nervous System.
The white paper proposes several updates to this system.
First, dissolve delays will be shortened, and reward levels will be lowered proportionally. This reduces long-term inflation while keeping governance participation attractive.
Second, the current linear reward bonus based on dissolve delay will be replaced with a convex curve. Short-term commitments will earn modest rewards, while multi-year staking will continue to receive stronger incentives.
Third, an explicit cap will be placed on the voting reward pool once the eight-year bootstrapping period ends. This ensures governance-related minting remains predictable.
Finally, maturity modulation will be simplified. Instead of complex formulas, maturity conversion into ICP will adjust based on deviations from long-term price levels.
Why Are Node Provider Rewards Being Reduced?
Node providers operate the physical infrastructure that runs the Internet Computer. Over time, DFINITY found that rewards for many nodes exceed actual operating costs.
The white paper highlights several inefficiencies:
- Many nodes are underutilized
- Legacy Gen-1 nodes receive higher rewards than necessary
- Future cloud engine workloads require a different provisioning model
To address this, Mission 70 proposes:
- Reducing rewards for Gen-1 nodes
- Shifting some capacity toward cloud engine infrastructure
- Increasing use of SEV-capable hardware to improve security with fewer nodes
These changes aim to better align payments with real infrastructure needs without weakening decentralization.
How Will Demand-Side Growth Reduce ICP Inflation?
The remaining 26% of inflation reduction must come from higher ICP burn. On the Internet Computer, computation is paid for using cycles, which are created by burning ICP.
At current price levels, DFINITY estimates that the cycle burn rate must rise from 0.05 XDR per second to 0.77 XDR per second to meet the Mission 70 target.
This increase is expected to come from expanded platform usage rather than artificial mechanisms.
Key demand drivers include:
- Onchain cloud engines for enterprise workloads
- AI-powered development platforms such as Caffeine
- Growth in self-writing cloud applications
- Increased adoption of canister-based applications
Notably, the paper points out that burn rates already exceeded this level for several months in 2025, suggesting the target is achievable.
What Role Do Onchain Cloud Engines Play?
Onchain cloud engines are designed to bring enterprise workloads directly onto the Internet Computer. Unlike traditional cloud services, these systems link usage directly to ICP burn.
Each computation increases demand for cycles, which reduces circulating supply.
DFINITY argues this creates a direct connection between real-world usage and token economics. As enterprises deploy applications, ICP burn rises in proportion to activity.
This model contrasts with networks where usage does not meaningfully affect supply.
How Does Caffeine Support Adoption And Demand?
Caffeine is a self-writing development platform that allows users to create applications using natural language. Instead of writing code, users interact with AI through chat and documents.
For non-technical users, this lowers the barrier to entry. For the network, it increases application deployment and compute usage.
Platforms like Caffeine align with what DFINITY calls the “self-writing cloud” paradigm, where application creation becomes accessible to a broader audience.
Higher adoption leads directly to increased ICP burn through computational fees.
What Is The Internet Computer And How Does It Work?
The Internet Computer is a decentralized network designed to run applications entirely onchain. Unlike traditional blockchains, it can host full-stack applications without relying on centralized cloud providers.
Applications run inside canisters, which are smart contracts capable of handling storage, computation, and user interactions.
This design supports complex operations in a secure, verifiable environment.
How Is The Internet Computer Being Used Today?
Institutional integrations show how the network is being applied beyond experiments.
Partnerships with Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud allow enterprises to integrate blockchain-based workflows into existing systems.
Fiat on-ramps introduced through FinchPay in November 2025 enable users to purchase ICP using Visa, Mastercard, and local payment methods such as PIX in Brazil and SPEI in Mexico.
As of November 2025, over 420,000 neurons are fully indexed and publicly accessible, reflecting growing participation in governance.
What Were The Major Internet Computer Advances In 2025?
Several technical milestones in 2025 support Mission 70’s demand assumptions.
AI Integrations And Tools
Caffeine AI launched in July, enabling chat-based development workflows. Developers report faster prototyping for simple canister deployments, though costs for larger models remain a factor.
Integrations with Facebook and Instagram in November expanded potential use cases, while projects like Ignition and Vertex advanced onchain AI inference.
Chain Fusion And Interoperability
Chain Fusion enables smart contracts to interact directly with external blockchains. Solana connectivity through the Helium milestone reduced reliance on traditional bridges.
Additional milestones support Bitcoin, EVM chains, and Dogecoin, placing the Internet Computer among networks pursuing native interoperability.
Privacy And Security Features
VetKeys enable encrypted threshold key management, supporting use cases like sealed auctions and private messaging.
Tools such as CryptoCheck show how privacy and AML compliance can coexist.
Identity And User Experience Improvements
Internet Identity 2.0 introduced passkeys and sign-ins via Google, Apple, and Microsoft. The Pulse milestone simplified authentication flows, while Plexus improved verifiable credentials.
Compute And Scalability Enhancements
Subnet storage expanded to 2 terabytes per subnet, totaling 94 terabytes across the network. HTTP gateways now allow browsers to interact directly with canisters.
Subnet splitting and canister snapshots improve scalability and resilience.
Conclusion
The Mission 70 white paper outlines a detailed and measurable plan to rebalance the Internet Computer’s tokenomics as the network matures. By reducing voting and node rewards while accelerating ICP burn through real usage, DFINITY aims to make inflation predictable and aligned with activity.
Rather than proposing abstract goals, the document focuses on execution, timelines, and quantitative targets. Mission 70 marks a move away from early-stage bootstrapping incentives and toward sustained, long-term operational discipline for the Internet Computer network.
Resources
Research paper authored by Dominic Williams, Founder and Chief Scientist at the DFINITY Foundation: Mission 70 and Accelerating the Internet Computer Economy
Dfinity Foundation on X: Post on Jan. 14
The SWOP on YouTube: Major ICP Updates
Read Next...
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Mission 70?
Mission 70 is DFINITY’s plan to reduce ICP inflation by at least 70% by the end of 2026 through supply reductions and increased network usage.
How Much Will ICP Inflation Be Reduced?
DFINITY projects inflation will fall from 9.72% in January 2026 to 2.92% by year-end if targets are met.
Does Mission 70 Change How ICP Is Used?
ICP continues to be used for governance, staking, and computation, but reward structures and burn dynamics will be adjusted.
Disclaimer
Disclaimer: The views expressed in this article do not necessarily represent the views of BSCN. The information provided in this article is for educational and entertainment purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice, or advice of any kind. BSCN assumes no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the information provided in this article. If you believe that the article should be amended, please reach out to the BSCN team by emailing [email protected].
Author
 Soumen Datta
Soumen DattaSoumen has been a crypto researcher since 2020 and holds a master’s in Physics. His writing and research has been published by publications such as CryptoSlate and DailyCoin, as well as BSCN. His areas of focus include Bitcoin, DeFi, and high-potential altcoins like Ethereum, Solana, XRP, and Chainlink. He combines analytical depth with journalistic clarity to deliver insights for both newcomers and seasoned crypto readers.
Crypto Project & Token Reviews
Project & Token Reviews
Comprehensive reviews of crypto's most interesting projects and assets
Learn about the hottest projects & tokens